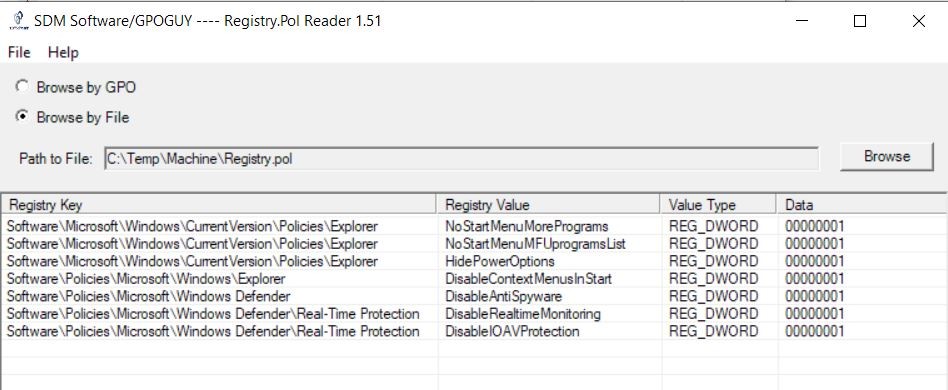
A completely routine tech support ticket has uncovered unexpected bans of IP addresses of Protonmail — a very useful service for people valuing their Internet freedoms — in several regions of Russia. I seriously didn’t want to sensationalize the headline, but the story is so strange and inexplicable I couldn’t resist.
TL;DR
Disclaimer: the situation is still developing. There might not be anything malicious, but most likely there is. I will update the post once new information comes through.
MTS and Rostelecom — two of the biggest Russian ISPs — started to block traffic to SMTP servers of the encrypted email service Protonmail according to an FSB request, with no regard for the official government registry of restricted websites. It seems like it’s been happening for a while, but no one paid special attention to it. Until now.
All involved parties have received relevant requests for information which they’re obligated to reply.
UPD: MTS has provided a scan of the FSB letter, which is the basis for restricting the access. Justification: the ongoing Universiade in Krasnoyarsk and “phone terrorism”. It’s supposed to prevent ProtonMail emails from going to emergency addresses of security services and schools.
UPD: Protonmail was surprised by “these strange Russians” and their methods for battling fraud abuse, as well as suggested a more effective way to do it — via abuse mailbox.
UPD: FSB’s justification doesn’t appear to be true: the bans broke ProtonMail’s incoming mail, rather than outgoing.
UPD: Protonmail shrugged and changed the IP addresses of their MXs taking them out of the blocking after that particular FSB letter. What will happen next is open ended question.
UPD: Apparently, such letter was not the only one and there is still a set of IP addresses of VOIP-services which are blocked without appropriate records in the official registry of restricted websites.



 Bangkok, in general, is a strange place to stay. Of course, it is warm there, rather cheap and some might find the cuisine interesting, along with the fact that about half of the world’s population
Bangkok, in general, is a strange place to stay. Of course, it is warm there, rather cheap and some might find the cuisine interesting, along with the fact that about half of the world’s population