Comments 54
Названо много pros за конвейеризацию, но забыты cons:
1) Бездумная конвейеризация там где не надо — это лишние задержки и лишний расход ресурсов, иногда значительный.
2) Алгоритмы с обратными связями (в обработке сигналов, к примеру) очень трудно конвейеризировать — либо просто мучительно больно с технической точки зрения, либо введение задержек изменяет сам алгоритм и сказывается на общей стабильности (качестве, характеристиках) системы.
А так здорово, ждем еще.
1) Бездумная конвейеризация там где не надо — это лишние задержки и лишний расход ресурсов, иногда значительный.
2) Алгоритмы с обратными связями (в обработке сигналов, к примеру) очень трудно конвейеризировать — либо просто мучительно больно с технической точки зрения, либо введение задержек изменяет сам алгоритм и сказывается на общей стабильности (качестве, характеристиках) системы.
А так здорово, ждем еще.
Спасибо) Вот и дискуссия появилась.
Обратную связь я упомянул)
С ЦОС я не работал: если более развернуто расскажете про проблемы, возникаемые там — будет замечательно)
Обратную связь я упомянул)
Бывает, схема к конвейризации не была готова, т.к. есть обратная связь, в связи с задержкой на такт(ы), начала неправильно работать.
С ЦОС я не работал: если более развернуто расскажете про проблемы, возникаемые там — будет замечательно)
Можно взять самый банальный пример рекурсивного фильтра x = k*a + (1-k)*x, где a — входные данные, x — выход, k — коэффициент от 0 до 1. На каждом такте в основной петле надо произвести умножение ( (1-k) * x) и сложение с k*a. Для макисмального быстродействия тут надо 3 такта как минимум, которых у нас нет.
Если вставлять задерки в петлю обратной связи, то характеристика фильтра начнет меняться и в конечном итоге рассыпется.
В общем алгоритмы с обратными связями (feed back) — зло, feed-forward — наше все! ;)
Если вставлять задерки в петлю обратной связи, то характеристика фильтра начнет меняться и в конечном итоге рассыпется.
В общем алгоритмы с обратными связями (feed back) — зло, feed-forward — наше все! ;)
Давно не занимаюсь ПЛИС, но статься понравилась, хорошо пишете :)
Если честно, AXI4-Stream я никогда не использовал. Если кто-то использовал оба интерфейса, буду признателен, если поделитесь сравнением и впечатлениями.
Судя по картинкам с временными диаграммами, ничем принципиально они не отличаются: двухфазное рукопожатие + полезная нагрузка. AMBA (включая AXI4) сейчас стала по сути промышленным стандартом, поэтому если будете покупать какой-то готовый IP-блок, то там скорей всего будет AXI.
По этой картинке я тоже принципиальной разницы не увидел, но у AXI4-Stream есть сигнал TUSER, который может быть произвольной длины. По описанию, туда можно положить какую-то информацию о пакете: к примеру, количество vlan'ов, чтобы знать с какого байта начинается IP-заголовок.
В этой ситуации я просто параллельно Avalon-ST добавляю еще одну структуру куда складываю информацию о пакете. Здесь это из коробки, что может быть удобно)
Еще есть сигнал TDEST, который явно показывает, куда (на какой порт) надо передать этот пакет, в Avalon-ST этого нет, приходится это добавлять в вышеупомянутую структуру)
В этой ситуации я просто параллельно Avalon-ST добавляю еще одну структуру куда складываю информацию о пакете. Здесь это из коробки, что может быть удобно)
Еще есть сигнал TDEST, который явно показывает, куда (на какой порт) надо передать этот пакет, в Avalon-ST этого нет, приходится это добавлять в вышеупомянутую структуру)
Прелесть Avalon-* интерфейсов в том, что перечень сигналов весьма гибок и можно пользоваться только теми, которые нужны, все остальное буде сделано шинной инфраструктурой автоматически. Это следствие того, что avalon «вырос» в мире FPGA.
Опыт работы с AXI у меня весьма эпизодический, но там, как я понимаю, есть фиксированный перечень сигналов в интерфейсе, который надо реализовывать всегда — из ARM это перешло и сюда.
Опыт работы с AXI у меня весьма эпизодический, но там, как я понимаю, есть фиксированный перечень сигналов в интерфейсе, который надо реализовывать всегда — из ARM это перешло и сюда.
Четырехфазное рукопожатие, ты хотел сказать
Хочу отметить, что во многих случаях можно обойтись без сигналов валидности. Простой сценарий: данные на вход поступают каждый квант времени, и проводят на каждой ступени конвейера один квант. Тут всё что нужно знать об устройстве в целом — длина конвейера, то есть количество ступеней. Я таким способом генерировал видео.
Конечно, если данные идут всегда, то смысла вводить сигнал валидности особо нет. С другой стороны, его задержанные братья будут явно показывать на какой стадии мы сейчас находимся, что может быть полезно при отладке.
Насчет «многих случаев»: думаю, всё-таки больше приложений, где данные идут не всегда, следовательно сигнал валидности нужен. Конечно, процент тех и других случаев вряд ли кто-то подсчитывал :)
Насчет «многих случаев»: думаю, всё-таки больше приложений, где данные идут не всегда, следовательно сигнал валидности нужен. Конечно, процент тех и других случаев вряд ли кто-то подсчитывал :)
IMHO
Использование always_comb, для такого кода в бонусе выдает, что это писал начинавший с программирования софта.
Железячник для простоты читаемости кода написал бы явный assign, без переприсвоения.
Использование always_comb, для такого кода в бонусе выдает, что это писал начинавший с программирования софта.
Железячник для простоты читаемости кода написал бы явный assign, без переприсвоения.
Думаю, дело вкуса. Мои коллеги не против, из минусов этой записи я вижу лишь то, что могут получиться два мультиплексора, которые стоят друг за другом, что не очень хорошо по частотке. Если такое вылезает, то приходится переделывать на case.
Либо еще есть какие-то минусы от такой записи?
P.S. Разве FPGA-шник должен быть железячником? :)
Либо еще есть какие-то минусы от такой записи?
P.S. Разве FPGA-шник должен быть железячником? :)
Если не затруднит, не могли бы Вы написать более читаемый вариант этого блока.
Я понимаю, как это можно описать при помощи assign, но тот вариант, который приходит на ум мне, не кажется более читаемым.
Может быть, Вы имеете в виду что-то другое.
Я понимаю, как это можно описать при помощи assign, но тот вариант, который приходит на ум мне, не кажется более читаемым.
Может быть, Вы имеете в виду что-то другое.
Кстати always в Верилоге довольно часто применяют для описания сложной комбинаторной логики, типа функций переходов автоматов и т.д. Гораздо нагляднее, чем городить?: (?: (?: (?: (? :)))).
Но вот код автора действительно приведет к куче ворнингов при синтезе, например про неиспользуемые биты в data_d2.
Лично мне религия не позволяет написать так, как автор — описание очень похоже на inferred latch, если не заметить строку «new_data_c = data_d1;», но думаю, что это уж точно дело вкуса.
Но вот код автора действительно приведет к куче ворнингов при синтезе, например про неиспользуемые биты в data_d2.
Лично мне религия не позволяет написать так, как автор — описание очень похоже на inferred latch, если не заметить строку «new_data_c = data_d1;», но думаю, что это уж точно дело вкуса.
Хм, загнал модуль в Квартус, но ни одного ворнинга не увидел.
Synplify Premier 2014.09:
@W:CL169: loop_l2.sv(30) | Pruning register data_d2[0][7:0]
@W:CL169: loop_l2.sv(30) | Pruning register data_d2[1][7:0]
@W:CL169: loop_l2.sv(30) | Pruning register data_d2[6][7:0]
@W:CL169: loop_l2.sv(30) | Pruning register data_d2[7][7:0]
@W:CL169: loop_l2.sv(30) | Pruning register data_d2[0][7:0]
@W:CL169: loop_l2.sv(30) | Pruning register data_d2[1][7:0]
@W:CL169: loop_l2.sv(30) | Pruning register data_d2[6][7:0]
@W:CL169: loop_l2.sv(30) | Pruning register data_d2[7][7:0]
Ага, закрадывалась мысль, что используете или Synplify, или Vivado.
Значит, Synplify более паранойный)
Защелкивание лишних данных мне никогда особо не мешало, но т.к. есть мысли переехать на Synplify, то, возможно, придется это учесть, спасибо!
Если не секрет, в своих проектах Вы от всех предупреждений избавляетесь?
Значит, Synplify более паранойный)
Защелкивание лишних данных мне никогда особо не мешало, но т.к. есть мысли переехать на Synplify, то, возможно, придется это учесть, спасибо!
Если не секрет, в своих проектах Вы от всех предупреждений избавляетесь?
Я сейчас сам не пишу код. Но поскольку наша контора продает RTL тем, кто делает ASIC-и, то к предупреждениям отношение очень серьезное. Наши индусы используют статический анализатор LEDA с нашим собственным набором правил (вроде бы, переделанным из IBM-овского), и релиз не пропустят, если есть хоть одно предупреждение. Если есть какие-то false-positive предупреждения, то они индивидуально маскируются.
Гораздо нагляднее, чем городить?: (?: (?: (?: (? :)))).
Для такого случая наглядней assign, тк есть переприсвание в начале на неупомянутые в if биты.
Это затрудняет понимание именно этого кода.
Куда понятней тот же код, где явно описано три возможных вариант в столбик и где (главное для понимания) определены все биты:
assign new_data_c = ()? {,} :
()? {,} :
{,};
Я обратил внимание, именно, на сложность интерпретации переприсваивания и возможных ошибок при этом.
Переприсваивание это строчка new_data_c = data_d1; вначале.
assign более явно описывает комбинаторную логику и сразу понятна ее реализация.
Там нельзя сделать переприсваивание и ошибки, только 3 явных и главное полных состояния выхода.
Переприсваивание это строчка new_data_c = data_d1; вначале.
assign более явно описывает комбинаторную логику и сразу понятна ее реализация.
Там нельзя сделать переприсваивание и ошибки, только 3 явных и главное полных состояния выхода.
Я прекрасно понимаю, что это может быть неинтуитивно для тех, кто так не писал :)
Возможную проблему с латчем, если кто-то удалит первую строчку я тоже знаю. Никаких нарушений канонов либо устоявшихся рекомендаций (например, смешивание блокирующих и неблокирующих присваиваний в одном always-блоке) в таком написании я не вижу.
Раньше я писал через assign как раз так, как Вы предлагаете, но у меня очень часто возникает задача в длинном слове поменять часть байт и через assign и кучу конкатенаций мне не нравилось делать, т.к. пишется много кода. Больше кода — больше ошибок: можно не те биты заменить, либо на один промазать, читаемость хуже…
Этот прием мне пришел в голову, когда я понял, что намного проще сначала присвоить, грубо говоря, default value, задержанное на несколько тактов, а потом уже его модифицировать, подменяя только нужные байты. Такая подмена это более высокоуровневое написание, чем assign, следовательно, должна быть более интуитивным и понятным. Думаю, дело вкуса и не более.
Возможную проблему с латчем, если кто-то удалит первую строчку я тоже знаю. Никаких нарушений канонов либо устоявшихся рекомендаций (например, смешивание блокирующих и неблокирующих присваиваний в одном always-блоке) в таком написании я не вижу.
Раньше я писал через assign как раз так, как Вы предлагаете, но у меня очень часто возникает задача в длинном слове поменять часть байт и через assign и кучу конкатенаций мне не нравилось делать, т.к. пишется много кода. Больше кода — больше ошибок: можно не те биты заменить, либо на один промазать, читаемость хуже…
Этот прием мне пришел в голову, когда я понял, что намного проще сначала присвоить, грубо говоря, default value, задержанное на несколько тактов, а потом уже его модифицировать, подменяя только нужные байты. Такая подмена это более высокоуровневое написание, чем assign, следовательно, должна быть более интуитивным и понятным. Думаю, дело вкуса и не более.
А как-нибудь так?
if ( startofpacket_d1 )
new_data_c = { data_d1[1:0], data_i[7:4], data_d1[7:6] };
else if ( startofpacket_o )
new_data_c = {data_d2[5:2], data_d1[3:0]};
else
new_data_c = data_d1;
Можно и так, но добавилась «лишняя» информация в ввиде data_d1[3:0]. :) Большой разницы через assign либо через так как Вы предложили я не вижу.
Мне приходится со структурами похожую операцию проделывать:
Как это красиво переписать без первой строчки?
Мне приходится со структурами похожую операцию проделывать:
typedef struct packed {
logic [7:0] a;
logic [7:0] b;
logic [7:0] c;
} s_t;
s_t s_comb;
s_t s_input;
s_t s_delayed; // задержанная на несколько тактов s_input
// подменяем в s_delayed только поле c
always_comb
begin
s_comb = s_delayed;
if( some_flag )
s_comb.c = 8'd42;
end
Как это красиво переписать без первой строчки?
SystemVerilog вас до добра не доведет :D
На самом деле, я видел код «с первой строчкой» и в чистом Верилоге — стандарту он не противоречит, а все остальное — дело привычки. LEDA на такое не ругается :)
На самом деле, я видел код «с первой строчкой» и в чистом Верилоге — стандарту он не противоречит, а все остальное — дело привычки. LEDA на такое не ругается :)
SystemVerilog реально крутая вещь)
Для меня не очень понятны советы новичкам, которые спрашивают «VHDL или Verilog?», и ему отвечают Verilog, мол он проще и похож на С. Должен быть спор VHDL vs SystemVerilog) Сейчас всё быстро меняется, и если надо разрабатывать большие проекты, то там только SystemVerilog ИМХО. (Хотя от приложения зависит, может если тим DSP, то тех извращений, что я делаю с данными, там не надо делать)
Правда, насколько я знаю, есть проблема в том, что не все синтезаторы поддерживают, но Synplify вроде впереди планеты всей и всё поддерживает)
Для меня не очень понятны советы новичкам, которые спрашивают «VHDL или Verilog?», и ему отвечают Verilog, мол он проще и похож на С. Должен быть спор VHDL vs SystemVerilog) Сейчас всё быстро меняется, и если надо разрабатывать большие проекты, то там только SystemVerilog ИМХО. (Хотя от приложения зависит, может если тим DSP, то тех извращений, что я делаю с данными, там не надо делать)
Правда, насколько я знаю, есть проблема в том, что не все синтезаторы поддерживают, но Synplify вроде впереди планеты всей и всё поддерживает)
А сейчас это полный аналог assign. (если поставить неблокирующее присвоение иначе приоритет будет неправильный)
И тут как раз кому как нравится визуально.
И тут как раз кому как нравится визуально.
Удивлен, что раньше использовали assign, но аргументация такого перехода понятна.
Для себя, если придется править, то может и быстрее. Но вот если передавать код, то другому разобраться в нем сложнее.
Просто всегда встречал такой код у тех, кто из программирования пришел к написанию RTL.
Для себя, если придется править, то может и быстрее. Но вот если передавать код, то другому разобраться в нем сложнее.
Просто всегда встречал такой код у тех, кто из программирования пришел к написанию RTL.
Единственное, для большей компактности можно было бы убрать begin/end вокруг однострочных блоков.
А так, на мой взгляд, более читаемое описание тут вряд ли получится.
А так, на мой взгляд, более читаемое описание тут вряд ли получится.
Что касается стандарта AXI4-Stream (а также AXI4 и AXI4-Lite), то они в целом довольно удобные для использования, с некоторыми исключениями.
Для управления процессом передачи данных используется два сигнала — TVALID и TREADY. TVALID поступает от источника и сигнализирует готовность данных на шине, TREADY поступает от приемника и подтверждает прием.
Если приемник уверен, что сможет сразу принять хотя бы одно слово данных от источника — то он может выставить изначально TREADY=1. В этом случае передача одного слова занимает один такт. Если же приемник не уверен (допустим, способность сразу принять данные зависит от их адреса) — то он должен выставить исходно TREADY=0, и тогда передача данных продлится минимум два такта. Стандарт запрещает комбинационные (безрегистровые) связи между сигналами TVALID и TREADY, поэтому нельзя сначала проверить адрес и потом уже решить, могут ли данные быть приняты в этом же такте.
В AXI4 (которая с адресами) есть еще такая проблема, что при передаче пакетов (bursts) нужно заранее знать длину пакета и выставить ее на шину. Нельзя передавать пакеты с неизвестной заранее длиной. Вернее сказать, попытаться-то можно, но приемник не обязан принимать данные (может выставить TREADY=0) до тех пор, пока ему не будет предоставлена информация о длине. Такое соглашение приводит к необходимости применения лишних буферов и логики там, где без них можно было бы обойтись.
Еще одна проблема, присутствующая в AXI4 и AXI4-Lite — это то, что ведущее устройство (master) может запросить данные из ведомого (slave) и при этом не быть готово к их приему. Допустим, процессор считывает содержимое одного из регистров периферийного устройства. Как правило, такие регистры подключаются к шине данных через мультиплексор, который выбирает нужный регистр в зависимости от адреса. Так вот, к тому моменту, когда процессор будет готов принять данные, он может уже снять адрес с шины адреса. Поэтому приходится либо запоминать адрес и держать его на мультиплексоре, либо запоминать считанные данные после мультиплексора — ставить лишний регистр. Ресурсы, ресурсы, такты…
Для управления процессом передачи данных используется два сигнала — TVALID и TREADY. TVALID поступает от источника и сигнализирует готовность данных на шине, TREADY поступает от приемника и подтверждает прием.
Если приемник уверен, что сможет сразу принять хотя бы одно слово данных от источника — то он может выставить изначально TREADY=1. В этом случае передача одного слова занимает один такт. Если же приемник не уверен (допустим, способность сразу принять данные зависит от их адреса) — то он должен выставить исходно TREADY=0, и тогда передача данных продлится минимум два такта. Стандарт запрещает комбинационные (безрегистровые) связи между сигналами TVALID и TREADY, поэтому нельзя сначала проверить адрес и потом уже решить, могут ли данные быть приняты в этом же такте.
В AXI4 (которая с адресами) есть еще такая проблема, что при передаче пакетов (bursts) нужно заранее знать длину пакета и выставить ее на шину. Нельзя передавать пакеты с неизвестной заранее длиной. Вернее сказать, попытаться-то можно, но приемник не обязан принимать данные (может выставить TREADY=0) до тех пор, пока ему не будет предоставлена информация о длине. Такое соглашение приводит к необходимости применения лишних буферов и логики там, где без них можно было бы обойтись.
Еще одна проблема, присутствующая в AXI4 и AXI4-Lite — это то, что ведущее устройство (master) может запросить данные из ведомого (slave) и при этом не быть готово к их приему. Допустим, процессор считывает содержимое одного из регистров периферийного устройства. Как правило, такие регистры подключаются к шине данных через мультиплексор, который выбирает нужный регистр в зависимости от адреса. Так вот, к тому моменту, когда процессор будет готов принять данные, он может уже снять адрес с шины адреса. Поэтому приходится либо запоминать адрес и держать его на мультиплексоре, либо запоминать считанные данные после мультиплексора — ставить лишний регистр. Ресурсы, ресурсы, такты…
Все это мелочи по сравнению с тем, что AXI может вернуть данные не в том порядке, в котором их попросил мастер.
Ну, это по желанию. В разделе А5.1 написано: «All transactions with a given AXI ID value must remain ordered, but there is no restriction on the ordering of transactions with different ID values». Эта же информация дублируется в разделе A6 во многих местах. Так что, если ведущее устройство хочет, чтобы все транзакции исполнялись в порядке поступления запросов, он может этого потребовать от шины и ведомых устройств.
Здесь есть один нюанс. В спецификации AXI сказано: «There are no ordering restrictions between read and write transactions with the same AWID and ARID. If a master requires an ordering restriction then it must ensure that the first transaction is fully completed before the second transaction is issued». (пункт 8.1 для AXI3 и 8.2 для AXI4),
Таким образом, действительно мастер может потребовать, чтобы все запросы на запись выполнялись по порядку, и все запросы на чтение тоже, но потребовать, чтобы запросы на запись и чтение не переупорядочивались между собой, он не может, даже если ARID и AWID будут одинаковы.
Таким образом, действительно мастер может потребовать, чтобы все запросы на запись выполнялись по порядку, и все запросы на чтение тоже, но потребовать, чтобы запросы на запись и чтение не переупорядочивались между собой, он не может, даже если ARID и AWID будут одинаковы.
Спасибо! Статья очень кстати. Как раз сейчас столкнулся с проблемами в работе своего проекта в железе. Похоже, что как раз «облако логики» не успевает. Есть о чем подумать.
И совсем не понял вот этот момент:
Почему так? Я вот ошибочно считал, что регистр будет запоминать данные по переднему фронту и проблема в том, что фронт клок придет раньше, чем установится состояние сумматоров, что приведет к тому, что запишется не то значение. Читаю про D-триггер, там речь о том, что по после переднего фронта С он начинает заносить значение в первый Т триггер и только после падения С уже подается на выход то, что там установилось. У вас же написано (и показано на картинках), что данные на выход попадут только по следующему переднему фронту CLK. Почему так?
И совсем не понял вот этот момент:
По положительному фронту (так называемый posedge) clk_i на вход модуля были поданы 4 числа: 4, 8, 15 и 23. На следующий положительный фронт в регистре no_pipe_res_o появился ответ 50
Почему так? Я вот ошибочно считал, что регистр будет запоминать данные по переднему фронту и проблема в том, что фронт клок придет раньше, чем установится состояние сумматоров, что приведет к тому, что запишется не то значение. Читаю про D-триггер, там речь о том, что по после переднего фронта С он начинает заносить значение в первый Т триггер и только после падения С уже подается на выход то, что там установилось. У вас же написано (и показано на картинках), что данные на выход попадут только по следующему переднему фронту CLK. Почему так?
Здесь есть тонкий момент, о котором я не написал, но подразумевал.
Считается, что схема полностью синхронная: вход x_i является выходом какого-то триггера, который тоже работает по clk_i. В первый posedge данные защелкнулись в триггер x_i, и стали валидны на его выходе. Весь такт сумматоры считают свои значения и на следующий положительный фронт сумма защелкнется в no_pipe_res_o.
Если честно, такого никогда не видел…
Считается, что схема полностью синхронная: вход x_i является выходом какого-то триггера, который тоже работает по clk_i. В первый posedge данные защелкнулись в триггер x_i, и стали валидны на его выходе. Весь такт сумматоры считают свои значения и на следующий положительный фронт сумма защелкнется в no_pipe_res_o.
Читаю про D-триггер, там речь о том, что по переднему фронту С он заносит значение в первый Т триггер и после падения С уже подается на выход.
Если честно, такого никогда не видел…
Возьмем такой пример:
Я специально сигналы a и b пересохраняю в триггер, что бы с триггера отдались данные на сумматоры.
Так выглядит функциональная симуляция в Квартусе (кстати 13):

Вот так временная:

Теперь представьте, что a/b_sync вынесены из этого модуля и выходы этих триггеров подаются на a_i, b_i в таком примере:
По поведению ничего не поменяется)
module some_example(
input clk_i,
input [7:0] a_i,
input [7:0] b_i,
output logic [7:0] no_pipe_res_o
);
logic [7:0] a_sync;
logic [7:0] b_sync;
logic [7:0] c;
always_ff @( posedge clk_i )
begin
a_sync <= a_i;
b_sync <= b_i;
end
assign c = a_sync + b_sync;
always_ff @( posedge clk_i )
begin
no_pipe_res_o <= c;
end
endmodule
Я специально сигналы a и b пересохраняю в триггер, что бы с триггера отдались данные на сумматоры.
Так выглядит функциональная симуляция в Квартусе (кстати 13):

Вот так временная:

Теперь представьте, что a/b_sync вынесены из этого модуля и выходы этих триггеров подаются на a_i, b_i в таком примере:
module some_example_2(
input clk_i,
input [7:0] a_i,
input [7:0] b_i,
output logic [7:0] no_pipe_res_o
);
always_ff @( posedge clk_i )
begin
no_pipe_res_o <= a_i + b_i;
end
endmodule
По поведению ничего не поменяется)
Немного адаптировал под Icarus
У меня в IcarusVerilog получилось так, что данные попадают на выход вообще сразу по переднему фронту.

Или мы вообще о разных вещах говорим? Verilog и SystemVerilog — ваш пример на чем? Что значит
no_pipe_example.v
module no_pipe_example(
input clk_i,
input [7:0] x_1,
input [7:0] x_2,
input [7:0] x_3,
input [7:0] x_4,
output logic [7:0] no_pipe_res_o
);
// no pipeline
always @( posedge clk_i )
no_pipe_res_o <= ( x_1 + x_2 ) + ( x_3 + x_4 );
endmodule
У меня в IcarusVerilog получилось так, что данные попадают на выход вообще сразу по переднему фронту.

Или мы вообще о разных вещах говорим? Verilog и SystemVerilog — ваш пример на чем? Что значит
always_ff @( posedge clk_i )?Мои все примеры на SystemVerilog)
always_ff @( posedge clk_i ) в этом примере эквивалентен always @( posedge clk_i ).
Попробуйте пример из сообщения чуть выше с sync подать в симуляцию, подав данные не по положительному фронту)
Какой конструкцией подаете сигналы x1-4 в Вашем примере?
always_ff @( posedge clk_i ) в этом примере эквивалентен always @( posedge clk_i ).
Попробуйте пример из сообщения чуть выше с sync подать в симуляцию, подав данные не по положительному фронту)
Какой конструкцией подаете сигналы x1-4 в Вашем примере?
Мне кажется, что вы подаете данные на tb конструкцией вида
Попробуйте вот так:
initial
begin
#100;
x_1 = 4;
x_2 = 8;
...
end
Попробуйте вот так:
initial
begin
@( posedge tb_clk )
x_1 <= 4;
x_2 <= 8;
...
end
А какой смысл так писать тестовые модули? Они должны выдавать сигналы во времени именно так, как у меня на графике, так, как данные в реальном времени подаются на вход модулей, а не промежуточных регистров. Если тестовый модуль писать тоже с posedge и в нем значения записывать через <=, то логично, то там может появиться еще один такт. Но зачем так делать?
По факту получается, что в статье есть 1) текст модулей 2) рисунок входных и выходных сигналов, который не соответствует действительности (вывод данных задерживается на такт у no_piped модуля и на 2 такта у piped), потому что входные сигналы подаются тоже через регистры, но о том, что они есть и как в них пишутся данные — мы не знаем. Надо как-то этот вопрос осветить, наверное.
По факту получается, что в статье есть 1) текст модулей 2) рисунок входных и выходных сигналов, который не соответствует действительности (вывод данных задерживается на такт у no_piped модуля и на 2 такта у piped), потому что входные сигналы подаются тоже через регистры, но о том, что они есть и как в них пишутся данные — мы не знаем. Надо как-то этот вопрос осветить, наверное.
Смысл заключается в том, что бы сделать так, что бы эти сигналы были синхронны с клоком.
Попробуйте следующий пример:
Модуль 1:
Модуль 2:
Просто просимулируйте и скиньте сюда картинку) В этом примере x_1-4 идут с триггеров.
Попробуйте следующий пример:
Модуль 1:
module gen_x(
input clk_i,
input rst_i,
output logic [7:0] x_1_o,
output logic [7:0] x_2_o,
output logic [7:0] x_3_o,
output logic [7:0] x_4_o
);
always @( posedge clk_i or posedge rst_i )
if( rst_i )
begin
x_1_o <= '0;
x_2_o <= '0;
x_3_o <= '0;
x_4_o <= '0;
end
else
begin
x_1_o <= x_1_o + 8'd1;
x_2_o <= x_2_o + 8'd3;
x_3_o <= x_3_o + 8'd5;
x_4_o <= x_4_o + 8'd7;
end
endmodule
Модуль 2:
module top(
input clk_i,
input rst_i,
output logic [7:0] no_pipe_res_o
);
logic [7:0] x_1_w;
logic [7:0] x_2_w;
logic [7:0] x_3_w;
logic [7:0] x_4_w;
gen_x gen_x(
.clk_i ( clk_i ),
.rst_i ( rst_i ),
.x_1_o ( x_1_w ),
.x_2_o ( x_2_w ),
.x_3_o ( x_3_w ),
.x_4_o ( x_4_w )
);
no_pipe_example no_pipe(
.clk_i ( clk_i )
.x_1 ( x_1_w ),
.x_2 ( x_2_w ),
.x_3 ( x_3_w ),
.x_4 ( x_4_w ),
.no_pipe_res_o ( no_pipe_res_o )
);
Просто просимулируйте и скиньте сюда картинку) В этом примере x_1-4 идут с триггеров.
Просимулирую, но уже позже (
А в реальной жизни сигналы синхронны с клоком?
А в реальной жизни сигналы синхронны с клоком?
Зависит от того, что Вы вкладываете в слово «реальная жизнь».
В симуляторе мы отсматриваем модель того, что происходит в жизни. Есть модель функциональная, а есть временная. Еще можно симулировать не RTL-код, а нетлист или гейты, и тогда еще более реальная жизнь происходит. Когда мы выбираем какой-то тип симуляции, то соглашаемся с теми допущениями, что в ней есть. Все эти картинки, это лишь то, как симулятор видит нашу схему на тех входных воздействиях, что в нее подали)
Разницу между функциональной и временной можно увидеть выше.
К сожалению, из литературы по верификации мне ничего не приходит в голову хорошого и простого. Есть «SystemVerilog for Verification», там есть глава Connecting Testbench and Design, но там чисто SystemVerilog'овские штуки раскрываются и может быть всё усложнено. Посмотрите примеры на testbench.in / asic-world.com, например, www.asic-world.com/examples/verilog/arbiter.html
В симуляторе мы отсматриваем модель того, что происходит в жизни. Есть модель функциональная, а есть временная. Еще можно симулировать не RTL-код, а нетлист или гейты, и тогда еще более реальная жизнь происходит. Когда мы выбираем какой-то тип симуляции, то соглашаемся с теми допущениями, что в ней есть. Все эти картинки, это лишь то, как симулятор видит нашу схему на тех входных воздействиях, что в нее подали)
Разницу между функциональной и временной можно увидеть выше.
К сожалению, из литературы по верификации мне ничего не приходит в голову хорошого и простого. Есть «SystemVerilog for Verification», там есть глава Connecting Testbench and Design, но там чисто SystemVerilog'овские штуки раскрываются и может быть всё усложнено. Посмотрите примеры на testbench.in / asic-world.com, например, www.asic-world.com/examples/verilog/arbiter.html
В реальной жизни это зависит от сигналов. Если сигнал идет от АЦП с синхронным интерфейсом, который вы сами тактируете, то они будут синхронными. Если сигнал идет с кнопок, или с UART-а, или с другого устройства, которое работает на своей собственной частоте, независимой от частоты ПЛИС, то они не будут синхронными. В этом случае возможен вариант, когда входные сигналы изменятся слишком близко ко фронту клока в ПЛИС, что приведет к нарушению времени предустановки триггеров (setup violation). С этим можно бороться путем добавления синхронизаторов
Чтобы была видна разница, я решил три теста одновременно показать в симуляторе:
test0 — данные идут с триггеров gen_x.
test1 — данные по @( posedge clk ) делаются.
test2 — данные по #20 выставляются.
Код:
Если что, no_pipe_example — тот, который под Icarus «адаптирован».
А вот и симуляция:
Несмотря на то, что по картинке test0_x*, test1_x*, test2_x* полностью идентичны, симулятор их совершенно по разному воспринимает: test0 и test1 полностью идентичны, а test2 выполняет всё на такт раньше)
test0 — данные идут с триггеров gen_x.
test1 — данные по @( posedge clk ) делаются.
test2 — данные по #20 выставляются.
Код:
Скрытый текст
module top_tb;
logic clk;
logic rst;
initial
begin
clk = 1'b0;
forever
begin
#10;
clk = !clk;
end
end
initial
begin
rst = 1'b0;
#2;
rst <= 1'b1;
#2;
rst <= 1'b0;
end
// ********** TEST 0 ***********
logic [7:0] test0_res_w;
logic [7:0] test0_x_1_w;
logic [7:0] test0_x_2_w;
logic [7:0] test0_x_3_w;
logic [7:0] test0_x_4_w;
gen_x gen_x(
.clk_i ( clk ),
.rst_i ( rst ),
.x_1_o ( test0_x_1_w ),
.x_2_o ( test0_x_2_w ),
.x_3_o ( test0_x_3_w ),
.x_4_o ( test0_x_4_w )
);
no_pipe_example no_pe_0(
.clk_i ( clk ),
.x_1 ( test0_x_1_w ),
.x_2 ( test0_x_2_w ),
.x_3 ( test0_x_3_w ),
.x_4 ( test0_x_4_w ),
.no_pipe_res_o ( test0_res_w )
);
// ********** TEST 1 ***********
logic [7:0] test1_res_w;
logic [7:0] test1_x_1_w;
logic [7:0] test1_x_2_w;
logic [7:0] test1_x_3_w;
logic [7:0] test1_x_4_w;
initial
begin
test1_x_1_w = '0;
test1_x_2_w = '0;
test1_x_3_w = '0;
test1_x_4_w = '0;
for( int i = 1; i < 10; i++ )
begin
@( posedge clk );
test1_x_1_w <= i*1;
test1_x_2_w <= i*3;
test1_x_3_w <= i*5;
test1_x_4_w <= i*7;
end
end
no_pipe_example no_pe_1(
.clk_i ( clk ),
.x_1 ( test1_x_1_w ),
.x_2 ( test1_x_2_w ),
.x_3 ( test1_x_3_w ),
.x_4 ( test1_x_4_w ),
.no_pipe_res_o ( test1_res_w )
);
// ********** TEST 2 ***********
logic [7:0] test2_res_w;
logic [7:0] test2_x_1_w;
logic [7:0] test2_x_2_w;
logic [7:0] test2_x_3_w;
logic [7:0] test2_x_4_w;
initial
begin
test2_x_1_w = '0;
test2_x_2_w = '0;
test2_x_3_w = '0;
test2_x_4_w = '0;
#10;
for( int i = 1; i < 10; i++ )
begin
test2_x_1_w = i*1;
test2_x_2_w = i*3;
test2_x_3_w = i*5;
test2_x_4_w = i*7;
#20;
end
end
no_pipe_example no_pe_2(
.clk_i ( clk ),
.x_1 ( test2_x_1_w ),
.x_2 ( test2_x_2_w ),
.x_3 ( test2_x_3_w ),
.x_4 ( test2_x_4_w ),
.no_pipe_res_o ( test2_res_w )
);
endmodule
Если что, no_pipe_example — тот, который под Icarus «адаптирован».
А вот и симуляция:
Скрытый текст

Несмотря на то, что по картинке test0_x*, test1_x*, test2_x* полностью идентичны, симулятор их совершенно по разному воспринимает: test0 и test1 полностью идентичны, а test2 выполняет всё на такт раньше)
Мои все примеры на SystemVerilog)А в чем разница, если в двух словах? Я вот только с приведением типов столкнулся.
Тестовый такой:
testbench.v
module testbench();
reg tb_clk;
reg [7:0] x_1,x_2,x_3,x_4;
wire [7:0] res, res_pipe;
no_pipe_example ex1(tb_clk,x_1,x_2,x_3,x_4,res);
pipe_example ex2(tb_clk,x_1,x_2,x_3,x_4,res_pipe);
initial
begin
$dumpfile("bench.vcd");
$dumpvars(0,testbench);
tb_clk = 0;
#50;
x_1 = 4;
x_2 = 8;
x_3 = 15;
x_4 = 23;
#100;
tb_clk = 1;
#100;
tb_clk = 0;
#100;
x_1 = 0;
x_2 = 0;
x_3 = 0;
x_4 = 0;
tb_clk = 1;
#100;
tb_clk = 0;
#100;
tb_clk = 1;
#100;
tb_clk = 0;
end
initial begin
end
endmodule
pipe_example.v
module pipe_example(
input clk_i,
input [7:0] x_1,
input [7:0] x_2,
input [7:0] x_3,
input [7:0] x_4,
output logic [7:0] pipe_res_o
);
// pipeline
logic [7:0] s1 = 0;
logic [7:0] s2 = 0;
always @( posedge clk_i )
begin
s1 <= ( x_1 + x_2 );
s2 <= ( x_3 + x_4 );
pipe_res_o <= s1 + s2;
end
endmodule
Получается вот что
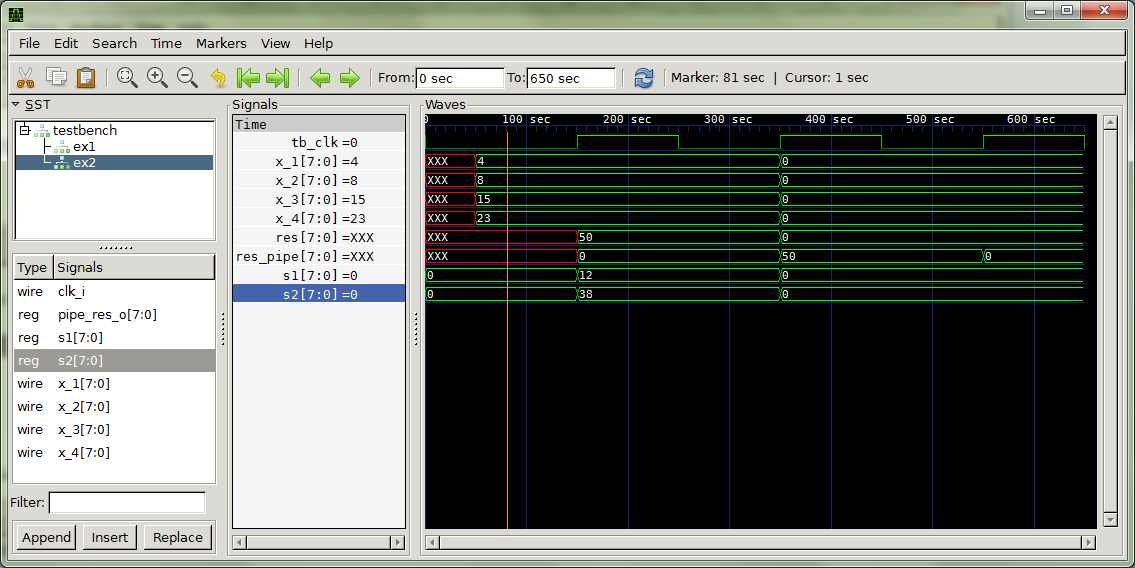
Отставание на 1 такт piped модуля вопросов как раз и не вызывает. Суть моих «непоняток» как раз в том, почему данные на выходе no_pipelined модуля со второго такта? Видать такой тест или что-то еще есть в проекте, о чем в тексте не указано. Это ж запутывает, во всяком случае меня :)
SystemVerilog это продолжение стандарта Verilog.
Туда добавили кучу новых плюшек, как синтезируемых, так и не синтезируемых, которые упрощают и убыстряют разработку.
Я предлагаю вынести создание клока в отдельный initial, что бы он не мешался.
В вашем примере вы явно не сообщаете симулятору, что x_* это сигналы, которые привязаны (либо синхронны) с tb_clk. Для того, что бы это указать можно использовать @( posedge tb_clk ) или сделать clocking block и писать что-то типа @cb.
Попробуйте так:
Туда добавили кучу новых плюшек, как синтезируемых, так и не синтезируемых, которые упрощают и убыстряют разработку.
Я предлагаю вынести создание клока в отдельный initial, что бы он не мешался.
В вашем примере вы явно не сообщаете симулятору, что x_* это сигналы, которые привязаны (либо синхронны) с tb_clk. Для того, что бы это указать можно использовать @( posedge tb_clk ) или сделать clocking block и писать что-то типа @cb.
Попробуйте так:
initial
begin
tb_clk = 1'b0;
forever
begin
#100;
tb_clk = !tb_clk;
end
end
initial
begin
@( posedge tb_clk );
x_1 <= 4;
x_2 <= 8;
x_3 <= 15;
x_4 <= 23;
@( posedge tb_clk );
x_1 <= 0;
x_2 <= 0;
x_3 <= 0;
x_4 <= 0;
end
Sign up to leave a comment.


Пару слов о конвейерах в FPGA