Comments 56
Отличная программа. Мы с группой энтузиастов с SQL.RU (много флуда) перевели ее на десяток разных языков программирования, чтобы сравнить вычислительную скорость. Есть проект на гитхабе с результатами.
Один из промежуточных более-менее полных результатов
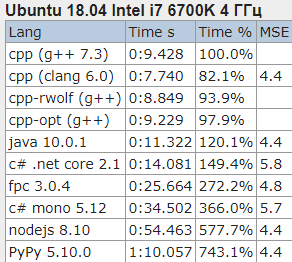
В результате победила с небольшим перевесом версия на С со вставками SSE4 инструкций.
github.com/Mark-Kovalyov/CardRaytracerBenchmark
пых, как и родной питон работали примерно с такой вот «скоростью»
Там написано "ПОСОНЫ НЕ КАЧАЙТЕ ТАМ ВИРУС"?)))))))))))
Непонятно правда почему был выбран PyPy вместо эталонной реализации?

Оригинальный троллинг, ящитаю.
caniuse.com/#feat=webp
На ипхоне тоже не отображается
PICTURE с fallback-изображением в формате PNG.В этом способе из источников испускаются тысячи лучей на пиксель и программа следит за ними, надеясь, что он найдут источник освещения.
Поясните плз. Из источника в источник?
Чисто теоретически, его можно запустить на мк с внешней памятью?
А можно покрутить сцену? Интересно, что наверху и с другой стороны :)
Посмотрим как он ответит.
Косяки следующие:
Функция testSphere() возвращает -1 для точки A (то есть она снаружи) и 1 для B (то есть она внутри). Знаки у расстояний — это просто трюк, позволяющий получить два элемента информации вместо одного в случае одного значения. Подобный тип функции можно написать и для описания параллелограмма (именно это и выполняется в функции function BoxTest).
Судя по коду и комменту к нему, это всё же расстояние до сферы, если быть точнее, до её поверхности.
// Signed distance point(p) to sphere(c,r)
float testSphere(Vec p, Vec c, float r) {
Vec delta = c - p;
float distance = sqrtf(delta%delta);
return radius - distance;
} Ну и наконец о том, что тут коммент лучше названия:
// Sample the world using Signed Distance Fields.
float QueryDatabase(Vec position, int &hitType) {Ибо это действительно функция которая считает Distance Field.
А ещё, есть сильные подозрения что…
В коде нет вершин. Всё выполняется с помощью функций CSG.
Что CSG тут не причём. А всё выполняется с помощью SDF функций.
Знак при этом вовсе не трюк, а побочный эффект простой реализации функции. Кроме того он играет роль при комбинировании моделей.
Просто картинка при 4096 сэмплах, не зря же ноут 10 часов мне воздух грел :)
Хотя я от картинки с 2048 сэмплами из статьи разницы не увидел

char letters[15*4+1] = // 15 two points lines
"5O5_" "5W9W" "5_9_" // P (without curve)
"AOEO" "COC_" "A_E_" // I
"IOQ_" "I_QO" // X
"UOY_" "Y_]O" "WW[W" // A
"aOa_" "aWeW" "a_e_" "cWiO"; // R (without curve)
Сами знаете какое слово хочется написать.
Коды символов используются как координаты. Можно заменить на массив целых. x0 y0 — начало линии и x1 y1 — конец.
int letters[15*4+1] = {
// (x0, y0), (x1, y1)
// P (without curve)
53, 79, 53, 95,
53, 87, 57, 87,
53, 95, 57, 95,
// I
65, 79, 69, 79,
67, 79, 67, 95,
65, 95, 69, 95,
// X
73, 79, 81, 95,
73, 95, 81, 79,
// A
85, 79, 89, 95,
89, 95, 93, 79,
87, 87, 91, 87,
// R (without curve)
97, 79, 97, 95,
97, 87, 101, 87,
97, 95, 101, 95,
99, 87, 105, 79
};Вот здесь можете экспериментировать:
https://codepen.io/anon/pen/bOYjNJ
1drv.ms/u/s!Ai7NYx46sGsugdUAJBfOJMljf7BKJQ
Копипастим, onedrive спотыкается на восклицательном знаке.
Там же в комментариях написано without curve. Дугу из линий не построить, они дорисовываются вот тут:
// Two curves (for P and R in PixaR) with hard-coded locations.
Vec curves[] = {Vec(-11, 6), Vec(11, 6)};
for (int i = 2; i--;) {
Vec o = f + curves[i] * -1;
distance = min(distance,
o.x > 0 ? fabsf(sqrtf(o % o) - 2)
: (o.y += o.y > 0 ? -2 : 2, sqrtf(o % o))
);
}Ну да, чем ещё заниматься 1го января русскому программисту ^_^
А я наивно ждал другое слово:

Держите на Rust:
name = "pixar"
version = "0.1.0"
authors = ["AndrewKensler <xxx@xxx.xx>"]
edition = "2018"
[dependencies]
rand = "*"
png = "*"
indicatif = "*"
num_cpus = "*"
[profile.dev]
opt-level = 3const IS_HABR: bool = false;
const WIDTH: u32 = 960;
const HEIGHT: u32 = 540;
const SAMPLES_POW: u32 = 4;
const BOUNCE_COUNT: u32 = 3;
const HIT_NONE: u8 = 0;
const HIT_LETTER: u8 = 1;
const HIT_WALL: u8 = 2;
const HIT_SUN: u8 = 3;
#[derive(Copy, Clone)]
struct Vec3 {
x: f64,
y: f64,
z: f64,
}
impl Vec3 {
fn new(x: f64, y: f64, z: f64) -> Vec3 {
Vec3 { x, y, z }
}
fn repeat(v: f64) -> Vec3 {
Vec3::new(v, v, v)
}
fn zeros() -> Vec3 {
Vec3::repeat(0.)
}
#[allow(dead_code)]
fn rotate_x(self, c: f64) -> Vec3 {
Vec3::new(
self.x,
self.y * c.cos() - self.z * c.sin(),
self.y * c.sin() + self.z * c.cos(),
)
}
#[allow(dead_code)]
fn rotate_y(self, c: f64) -> Vec3 {
Vec3::new(
self.z * c.sin() + self.x * c.cos(),
self.y,
self.z * c.cos() - self.x * c.sin(),
)
}
#[allow(dead_code)]
fn rotate_z(self, c: f64) -> Vec3 {
Vec3::new(
self.x * c.cos() - self.y * c.sin(),
self.x * c.sin() + self.y * c.cos(),
self.z,
)
}
}
use ::std::ops::{Add, Mul, Not, Rem};
impl Add for Vec3 {
type Output = Vec3;
fn add(self, other: Vec3) -> Vec3 {
Vec3 {
x: self.x + other.x,
y: self.y + other.y,
z: self.z + other.z,
}
}
}
impl Add<f64> for Vec3 {
type Output = Vec3;
fn add(self, other: f64) -> Vec3 {
Vec3 {
x: self.x + other,
y: self.y + other,
z: self.z + other,
}
}
}
impl Mul for Vec3 {
type Output = Vec3;
fn mul(self, other: Vec3) -> Vec3 {
Vec3 {
x: self.x * other.x,
y: self.y * other.y,
z: self.z * other.z,
}
}
}
impl Mul<f64> for Vec3 {
type Output = Vec3;
fn mul(self, other: f64) -> Vec3 {
Vec3 {
x: self.x * other,
y: self.y * other,
z: self.z * other,
}
}
}
impl Rem for Vec3 {
type Output = f64;
fn rem(self, other: Vec3) -> f64 {
self.x * other.x + self.y * other.y + self.z * other.z
}
}
impl Not for Vec3 {
type Output = Vec3;
fn not(self) -> Vec3 {
self * (1. / (self % self).sqrt())
}
}
// Rectangle CSG equation. Returns minimum signed distance from
// space carved by
// lowerLeft vertex and opposite rectangle vertex upperRight.
fn box_test(position: Vec3, lower_left: Vec3, upper_right: Vec3) -> f64 {
let lower_left = position + lower_left * -1.;
let upper_right = upper_right + position * -1.;
-lower_left
.x
.min(lower_left.y)
.min(lower_left.z)
.min(upper_right.x)
.min(upper_right.y)
.min(upper_right.z)
}
fn min(a: f64, b: f64) -> f64 {
a.min(b)
}
// Sample the world using Signed Distance Fields.
fn query_database(position: Vec3, hit_type: &mut u8) -> f64 {
let mut distance = 1_000_000_000.0_f64;
let mut f = position; // Flattened position (z=0)
f.z = 0.;
if IS_HABR {
let letters = [
// X
(57, 79, 65, 95),
(57, 95, 65, 79),
// A
(69, 79, 73, 95),
(73, 95, 77, 79),
(71, 87, 75, 87),
// B (without curves)
(81, 79, 81, 95),
(81, 79, 85, 79),
(81, 87, 85, 87),
(81, 95, 85, 95),
// R (without curve)
(93, 79, 93, 95),
(93, 87, 97, 87),
(93, 95, 97, 95),
(95, 87, 101, 79),
];
for letter in letters.iter() {
let begin = Vec3::new(letter.0 as f64 - 79., letter.1 as f64 - 79., 0.) * 0.5;
let e = Vec3::new(letter.2 as f64 - 79., letter.3 as f64 - 79., 0.) * 0.5 + begin * -1.;
let o = f + (begin + e * (-((begin + f * -1.) % e / (e % e)).min(0.)).min(1.)) * -1.;
distance = distance.min(o % o); // compare squared distance.
}
} else {
let letters = [
// 15 two points lines
"5O5_", "5W9W", "5_9_", // P (without curve)
"AOEO", "COC_", "A_E_", // I
"IOQ_", "I_QO", // X
"UOY_", "Y_]O", "WW[W", // A
"aOa_", "aWeW", "a_e_", "cWiO", // R (without curve)
];
for letter in letters.iter() {
let points = letter.as_bytes();
let begin = Vec3::new(points[0] as f64 - 79., points[1] as f64 - 79., 0.) * 0.5;
let e = Vec3::new(points[2] as f64 - 79., points[3] as f64 - 79., 0.) * 0.5 + begin * -1.;
let o = f + (begin + e * (-((begin + f * -1.) % e / (e % e)).min(0.)).min(1.)) * -1.;
distance = distance.min(o % o); // compare squared distance.
}
}
distance = distance.sqrt(); // Get real distance, not square distance.
// Two curves (for P and R in PixaR) with hard-coded locations.
let curves = if IS_HABR {
vec![Vec3::new(3., 6., 0.), Vec3::new(3., 2., 0.), Vec3::new(9., 6., 0.)]
} else {
vec![Vec3::new(-11., 6., 0.), Vec3::new(11., 6., 0.)]
};
for curve in curves.iter() {
let mut o = f + *curve * -1.;
distance = distance.min(if o.x > 0. {
((o % o).sqrt() - 2.).abs()
} else {
o.y += if o.y > 0. { -2. } else { 2. };
(o % o).sqrt()
});
}
distance = (distance.powf(8.) + position.z.powf(8.)).powf(0.125) - 0.5;
*hit_type = HIT_LETTER;
let room_dist = min(
// min(A,B) = Union with Constructive solid geometry
//-min carves an empty space
-min(
// Lower room
box_test(
position,
Vec3::new(-30., -0.5, -30.),
Vec3::new(30., 18., 30.),
),
// Upper room
box_test(
position,
Vec3::new(-25., 17., -25.),
Vec3::new(25., 20., 25.),
),
),
box_test(
// Ceiling "planks" spaced 8 units apart.
Vec3::new(position.x.abs() % 8., position.y, position.z),
Vec3::new(1.5, 18.5, -25.),
Vec3::new(6.5, 20., 25.),
),
);
if room_dist < distance {
distance = room_dist;
*hit_type = HIT_WALL;
};
let sun = 19.9 - position.y; // Everything above 19.9 is light source.
if sun < distance {
distance = sun;
*hit_type = HIT_SUN;
}
return distance;
}
fn ray_marching(origin: Vec3, direction: Vec3, hit_pos: &mut Vec3, hit_norm: &mut Vec3) -> u8 {
let mut hit_type = HIT_NONE;
let mut no_hit_count = 0;
// Signed distance marching
let mut total_d = 0.;
while total_d < 100. {
*hit_pos = origin + direction * total_d;
let d = query_database(*hit_pos, &mut hit_type); // distance from closest object in world.
if d < 0.01 || no_hit_count > 99 {
*hit_norm = !Vec3::new(
query_database(*hit_pos + Vec3::new(0.01, 0., 0.), &mut no_hit_count) - d,
query_database(*hit_pos + Vec3::new(0., 0.01, 0.), &mut no_hit_count) - d,
query_database(*hit_pos + Vec3::new(0., 0., 0.01), &mut no_hit_count) - d,
);
return hit_type;
}
no_hit_count += 1;
total_d += d;
}
return 0;
}
fn trace(origin: Vec3, direction: Vec3) -> Vec3 {
let mut origin = origin;
let mut direction = direction;
let mut sampled_position = Vec3::zeros();
let mut normal = Vec3::zeros();
let mut color = Vec3::zeros();
let mut attenuation = Vec3::repeat(1.);
let light_direction = !Vec3::new(0.6, 0.6, 1.0);
let bounce_count = BOUNCE_COUNT;
for _ in 0..bounce_count {
let hit_type = ray_marching(origin, direction, &mut sampled_position, &mut normal);
if hit_type == HIT_NONE {
break;
} // No hit. This is over, return color.
if hit_type == HIT_LETTER {
// Specular bounce on a letter. No color acc.
direction = direction + normal * (normal % direction * -2.);
origin = sampled_position + direction * 0.1;
attenuation = attenuation * 0.2; // Attenuation via distance traveled.
}
if hit_type == HIT_WALL {
// Wall hit uses color yellow?
let incidence = normal % light_direction;
let p = 6.283185 * random_val();
let c = random_val();
let s = (1. - c).sqrt();
let g = if normal.z < 0. { -1. } else { 1. };
let u = -1. / (g + normal.z);
let v = normal.x * normal.y * u;
direction = Vec3::new(v, g + normal.y * normal.y * u, -normal.y) * p.cos() * s
+ Vec3::new(1. + g * normal.x * normal.x * u, g * v, -g * normal.x) * p.sin() * s
+ normal * c.sqrt();
origin = sampled_position + direction * 0.1;
attenuation = attenuation * 0.2;
if incidence > 0.
&& ray_marching(
sampled_position + normal * 0.1,
light_direction,
&mut sampled_position,
&mut normal,
) == HIT_SUN
{
color = color + attenuation * Vec3::new(500., 400., 100.) * incidence;
}
}
if hit_type == HIT_SUN {
//
color = color + attenuation * Vec3::new(50., 80., 100.);
break; // Sun Color
}
}
return color;
}
fn random_val() -> f64 {
rand::random()
}
fn get_sampling_points(pow: u32) -> Vec<(f64, f64)> {
let mut points = vec![];
let max = 1 << pow;
for a in 0..max {
let mut b = 0;
for i in 0..pow {
let mask_a = 1 << i;
let bit = (mask_a & a) != 0;
if bit {
let mask_b = 1 << (pow - i - 1);
b = b | mask_b;
}
}
points.push(((a as f64 + 0.5) / max as f64, (b as f64 + 0.5) / max as f64));
}
points
}
use std::time::Instant;
use std::thread;
extern crate indicatif;
use indicatif::{MultiProgress, ProgressBar, ProgressStyle};
fn main() {
let w = WIDTH as i32;
let h = HEIGHT as i32;
let samples_power = SAMPLES_POW;
let samples_count = 1 << samples_power;
let now = Instant::now();
let m = MultiProgress::new();
let sty = ProgressStyle::default_bar()
.template("[{elapsed_precise}] {bar:40.cyan/blue} {pos:>7}/{len:7} {eta_precise}")
.progress_chars("=>-");
let get_promise = move |y0, y1, pb: ProgressBar| -> Vec<u8> {
let sampling_points = &get_sampling_points(samples_power);
let position = Vec3::new(-22., 5., 25.);
let goal = !(Vec3::new(-3., 4., 0.) + position * -1.);
let left = Vec3::new(goal.z, 0., -goal.x) * (1. / w as f64);
let up = Vec3::new(
goal.y * left.z - goal.z * left.y,
goal.z * left.x - goal.x * left.z,
goal.x * left.y - goal.y * left.x,
);
let mut image_data: Vec<u8> = Vec::with_capacity((w * h * 3) as usize);
for y in y0..y1 {
for x in 0..w {
let x = (w / 2 - x) as f64;
let y = (h / 2 - y) as f64;
let mut color = Vec3::zeros();
for p in sampling_points {
let x = x + p.0;
let y = y + p.1;
color = color + trace(position, !(goal + left * x + up * y));
}
color = color * (1. / samples_count as f64) + 14. / 241.;
let o = color + 1.;
color = Vec3::new(color.x / o.x, color.y / o.y, color.z / o.z) * 255.;
image_data.push(color.x.max(0.).min(255.) as u8);
image_data.push(color.y.max(0.).min(255.) as u8);
image_data.push(color.z.max(0.).min(255.) as u8);
}
pb.inc(1);
}
pb.finish_with_message("done");
image_data
};
println!("Rendering...");
let mut promices = vec![];
let num_logical_cores = num_cpus::get() as i32;
for n in 0..num_logical_cores {
let fragment_size = h / num_logical_cores;
let y0 = fragment_size * n;
let y1 = if n == num_logical_cores - 1 {
h
} else {
fragment_size * (n + 1)
};
let length = (y1 - y0) as u64;
let pb = m.add(ProgressBar::new(length));
pb.set_style(sty.clone());
let promice = thread::spawn(move || {
get_promise(y0, y1, pb)
});
promices.push(promice);
}
m.join_and_clear().unwrap();
let mut image_data = Vec::new();
for promice in promices {
let mut thread_image_data = promice.join().unwrap();
image_data.append(&mut thread_image_data);
}
println!("{} sec", now.elapsed().as_secs());
let name = format!("{}_{:04}.png", if IS_HABR { "habr" } else { "pixar" }, samples_count);
let path = std::path::Path::new(&name);
let file = std::fs::File::create(path).unwrap();
let ref mut writer_1 = std::io::BufWriter::new(file);
let mut encoder = png::Encoder::new(writer_1, w as u32, h as u32);
use png::HasParameters;
encoder.set(png::ColorType::RGB).set(png::BitDepth::Eight);
let mut writer = encoder.write_header().unwrap();
writer.write_image_data(&image_data).unwrap();
}


Расшифровка трассировщика лучей размером с открытку