
Information Security *
Data protection
PVS-Studio Visits Apache Hive

For the past ten years, the open-source movement has been one of the key drivers of the IT industry's development, and its crucial component. The role of open-source projects is becoming more and more prominent not only in terms of quantity but also in terms of quality, which changes the very concept of how they are positioned on the IT market in general. Our courageous PVS-Studio team is not sitting idly and is taking an active part in strengthening the presence of open-source software by finding hidden bugs in the enormous depths of codebases and offering free license options to the authors of such projects. This article is just another piece of that activity! Today we are going to talk about Apache Hive. I've got the report — and there are things worth looking at.
Winning PHDays 9 The Standoff: The chronicle by the True0xA3 team
Vitaliy has published three detailed articles on Habr, two of which were dedicated to the description of the strategies that True0xA3 team used before and during the competition to secure this team the title of the winners. I felt that the only thing that those two articles were lacking was a summary in English so that a wider audience of readers could enjoy them. So, below is the summary of two articles by Vitaliy Malkin, together with images Vitaliy published to clarify his points. Vitaliy has OKed me doing the translation and publishing it.
What's the Use of Dynamic Analysis When You Have Static Analysis?
Security of mobile OAuth 2.0

Popularity of mobile applications continues to grow. So does OAuth 2.0 protocol on mobile apps. It's not enough to implement standard as is to make OAuth 2.0 protocol secure there. One needs to consider the specifics of mobile applications and apply some additional security mechanisms.
In this article, I want to share the concepts of mobile OAuth 2.0 attacks and security mechanisms used to prevent such issues. Described concepts are not new but there is a lack of the structured information on this topic. The main aim of the article is to fill this gap.
The Data Structures of the Plasma Cash Blockchain's State

Hello, dear Habr users! This article is about Web 3.0 — the decentralized Internet. Web 3.0 introduces the concept of decentralization as the foundation of the modern Internet. Many computer systems and networks require security and decentralization features to meet their needs. A distributed registry using blockchain technology provides efficient solutions for decentralization.
WAF through the eyes of hackers
 Today we’re going to talk about one of the modern security mechanism for web applications, namely Web Application Firewall (WAF). We’ll discuss modern WAFs and what they are based on, as well as bypass techniques, how to use them, and why you should never entirely rely on WAF. We’re speaking from the pentesters’ perspective; we’ve never developed WAFs and only collected data from open sources. Thus, we can only refer to our own experience and may be unaware of some peculiarities of WAFs.
Today we’re going to talk about one of the modern security mechanism for web applications, namely Web Application Firewall (WAF). We’ll discuss modern WAFs and what they are based on, as well as bypass techniques, how to use them, and why you should never entirely rely on WAF. We’re speaking from the pentesters’ perspective; we’ve never developed WAFs and only collected data from open sources. Thus, we can only refer to our own experience and may be unaware of some peculiarities of WAFs.Long journey to Tox-rs. Part 1

Hi everyone!
I like Tox and respect the participants of this project and their work. In an effort to help Tox developers and users, I looked into the code and noticed potential problems that could lead to a false sense of security. Since I originally published this article in 2016 (in Russian), many improvements have been made to Tox, and I lead a team that re-wrote secure Tox software from scratch using the Rust programming language (check out Tox-rs). I DO recommend using tox in 2019. Let's take a look what actually made us rewrite Tox in Rust.
Original article of 2016
There is an unhealthy tendency to overestimate the security of E2E systems only on the basis that they are E2E. I will present objective facts supplemented with my own comments for you to draw your own conclusions.
Spoiler: The Tox developers agree with my points and my source code pull request was accepted.
What is going to happen on February 1, 2020?
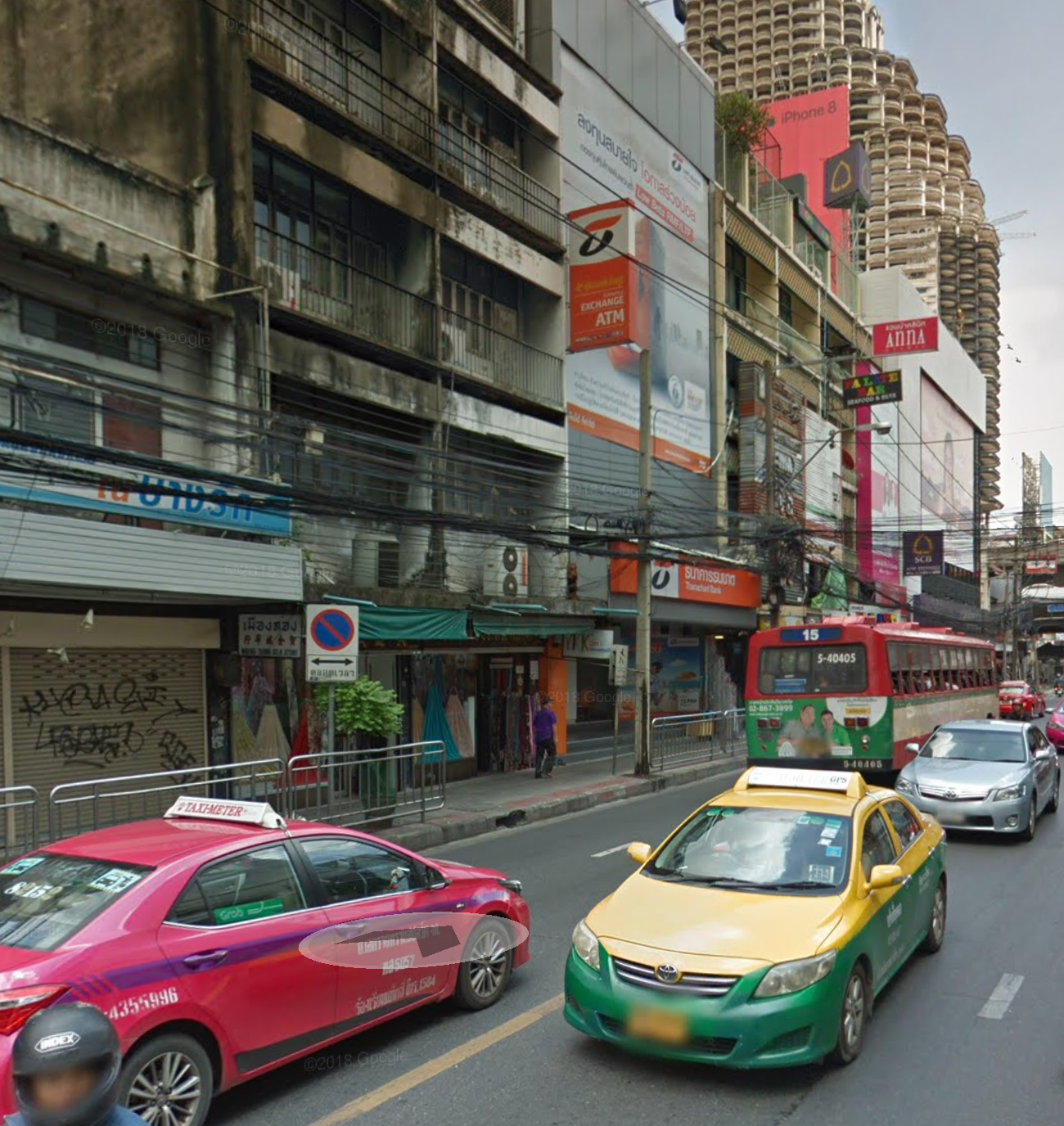 Bangkok, in general, is a strange place to stay. Of course, it is warm there, rather cheap and some might find the cuisine interesting, along with the fact that about half of the world’s population does not need to apply for a visa in advance to get there. However, you still need to get acquainted with the smells, and the city streets are casting cyberpunk scenes more than anything else.
Bangkok, in general, is a strange place to stay. Of course, it is warm there, rather cheap and some might find the cuisine interesting, along with the fact that about half of the world’s population does not need to apply for a visa in advance to get there. However, you still need to get acquainted with the smells, and the city streets are casting cyberpunk scenes more than anything else.In particular, a photo to the left has been taken not far from the center of Thailand’ capital city, one street away from the Shangri-La hotel, where the 30th DNS-OARC organization meeting took place on May 12 and 13. It is a non-profit organization dedicated to security, stability, and overall development of the DNS — the Domain Name System.
Slides from the DNS-OARC 30 meeting are recommended for everyone interested in how the DNS works, though perhaps the most interesting is what is absent in those slides. Namely, a 45-minute round table with a discussion around the results of DNS Flag Day 2019, which occurred on February, 1, 2019.
And, the most impressive result of a round table is the decision to repeat DNS Flag Day once again.
Digital Forensics Tips&Tricks: How to Find an Intruder's Lucky Coin

So, cyber attackers are do the same thing — they often hide some little malware agents in the IT Infrastructure to keep a possibility to come back again.
Even more secret Telegrams
We used to think of Telegram as a reliable and secure transmission medium for messages of any sort. But under the hood it has a rather common combination of a- and symmetric encryptions. Where’s fun in that? And why would anyone trust their private messages to a third-party anyway?

TL;DR — inventing a private covert channel through users blacklisting each other.
Legacy Outage
Right at the beginning, we need to outline a couple of details for our readers:
- All Autonomous System Numbers under 1000 are called “lower ASNs,” as they are the first autonomous systems on the Internet, registered by IANA in the early days (the late 80’s) of the global network. Today they mostly represent government departments and organizations, that were somehow involved in Internet research and creation in 70-90s.
- Our readers should remember, that the Internet became public only after the United States’ Department of Defense, which funded the initial ARPANET, handed it over to the Defense Communication Agency and, later in 1981, connected it to the CSNET with the TCP (RFC675)/IP (RFC791) over X.25. A couple of years later, in 1986, NSF swapped the CSNET in favor of NSFNET, which grew so fast it made possible ARPANET decommission by 1990.
- IANA was established in 1988, and supposedly at that time, existing ASNs were registered by the RIRs. It is no surprise that the organization that funded the initial research and creation of the ARPANET, further transferring it to another department because of its operational size and growth, only after diversifying it into 4 different networks (Wiki mentions MILNET, NIPRNET, SIPRNET and JWICS, above which the military-only NIPRNET did not have controlled security gateways to the public Internet).
Hack the JWT Token
For Educational Purposes Only! Intended for
Issue
The algorithm HS256 uses the secret key to sign and verify each message. The algorithm RS256 uses the private key to sign the message and uses the public key for authentication.
If you change the algorithm from RS256 to HS256, the backend code uses the public key as the secret key and then uses the HS256 algorithm to verify the signature. Asymmetric Cipher Algorithm => Symmetric Cipher Algorithm.
Because the public key can sometimes be obtained by the attacker, the attacker can modify the algorithm in the header to HS256 and then use the RSA public key to sign the data.
The backend code uses the RSA public key + HS256 algorithm for signature verification.
Example
Vulnerability appear when client side validation looks like this:
const decoded = jwt.verify(
token,
publickRSAKey,
{ algorithms: ['HS256' , 'RS256'] } //accepted both algorithms
)Lets assume we have initial token like presented below and " => " will explain modification that attacker can make:
//header
{
alg: 'RS256' => 'HS256'
}
//payload
{
sub: '123',
name: 'Oleh Khomaik',
admin: 'false' => 'true'
}The backend code uses the public key as the secret key and then uses the HS256 algorithm to verify the signature.
TLS 1.3 enabled, and why you should do the same

As we wrote in the 2018-2019 Interconnected Networks Issues and Availability Report at the beginning of this year, TLS 1.3 arrival is inevitable. Some time ago we successfully deployed the 1.3 version of the Transport Layer Security protocol. After gathering and analyzing the data, we are now ready to highlight the most exciting parts of this transition.
As IETF TLS Working Group Chairs wrote in the article:
“In short, TLS 1.3 is poised to provide a foundation for a more secure and efficient Internet over the next 20 years and beyond.”
TLS 1.3 has arrived after 10 years of development. Qrator Labs, as well as the IT industry overall, watched the development process closely from the initial draft through each of the 28 versions while a balanced and manageable protocol was maturing that we are ready to support in 2019. The support is already evident among the market, and we want to keep pace in implementing this robust, proven security protocol.
Eric Rescorla, the lone author of TLS 1.3 and the Firefox CTO, told The Register that:
“It's a drop-in replacement for TLS 1.2, uses the same keys and certificates, and clients and servers can automatically negotiate TLS 1.3 when they both support it,” he said. “There's pretty good library support already, and Chrome and Firefox both have TLS 1.3 on by default.”
Free Wireguard VPN service on AWS
Free Wireguard VPN service on AWS
The reasoning
The increase of Internet censorship by authoritarian regimes expands the blockage of useful internet resources making impossible the use of the WEB and in essence violates the fundamental right to freedom of opinion and expression enshrined in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
Article 19
Everyone has the right to freedom of opinion and expression; this right includes freedom to hold opinions without interference and to seek, receive and impart information and ideas through any media and regardless of frontiers.
The following is the detailed 6 steps instruction for non-IT people to deploy free* VPN service upon Wireguard technology in Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud infrastructure, using a 12 months free account, on an Instance (virtual machine) run by Ubuntu Server 18.04 LTS.
I tried to make this walkthrough as friendly as possible to people far from IT. The only thing required is assiduity in repeating the steps described below.
Zoo AFL

In this article, we're going to talk about not the classical AFL itself but about utilities designed for it and its modifications, which, in our view, can significantly improve the quality of fuzzing. If you want to know how to boost AFL and how to find more vulnerabilities faster – keep on reading!
The most common OAuth 2.0 Hacks
OAuth 2 overview
This article assumes that readers are familiar with OAuth 2. However, below a brief description of it is presented below.
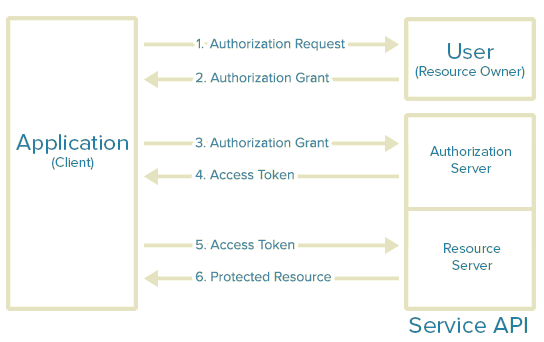
- The application requests authorization to access service resources from the user. The application needs to provide the client ID, client secret, redirect URI and the required scopes.
- If the user authorizes the request, the application receives an authorization grant
- The application requests an access token from the authorization server by presenting authentication of its own identity, and the authorization grant
- If the application identity is authenticated and the authorization grant is valid, the authorization server issues the access and refresh (if required) token to the application. Authorization is complete.
- The application requests the resource from the resource server and presents the access token for authentication
- If the access token is valid, the resource server serves the resource to the application
The are some main Pros and Cons in OAuth 2.0
- OAuth 2.0 is easier to use and implement (compared to OAuth 1.0)
- Wide spread and continuing growing
- Short lived Tokens
- Encapsulated Tokens
— No signature (relies solely on SSL/TLS ), Bearer Tokens
— No built-in security
— Can be dangerous if used from not experienced people
— Too many compromises. Working group did not make clear decisions
— Mobile integration (web views)
— Oauth 2.0 spec is not a protocol, it is rather a framework — RFC 6749
How to Set Up Your Own VPN Server in 15 Minutes
If you use Habr, chances are, you’re conscious about privacy on the web. As governments and corporations tighten their grip on people’s online activities, the issue of keeping your browsing data to yourself becomes more and more relevant.
Numerous tech websites say VPN is no longer a geek-only thing, and regular people should use it, too (Fast Company, Mashable, PCMag). But as a tech-savvy person, you know there isn’t a service you can trust as much as the one you host and manage yourself.
With this post, you’ll deploy your own instance of Outline VPN on AWS.
Google+ is Dead. So what?
Google shut down their social media platform Google+ on April 2, 2019. It’s hard to find some technical article that hasn’t mentioned the end of Google’s social network era. But, a high level of consistency in connectivity within services of the company had received scant attention. In this article I would like to share my thoughts on the internal way of Google services consistency and what it means for Google API users when it comes to a Google+ shutdown.
Bad news, everyone! New hijack attack in the wild
With this article, we want to show an example of the attack where not only the true attacker was under the question, but the whole list of affected prefixes. Moreover, it again raises concerns about the possible motives for the future attack of this type.
Authors' contribution
alizar 21696.3ptsecurity 10799.2marks 9200.7GlobalSign_admin 6670.9LukaSafonov 6217.4Kaspersky_Lab 5488.9ValdikSS 5478.6ru_vds 3476.6esetnod32 3275.0zhovner 2947.0