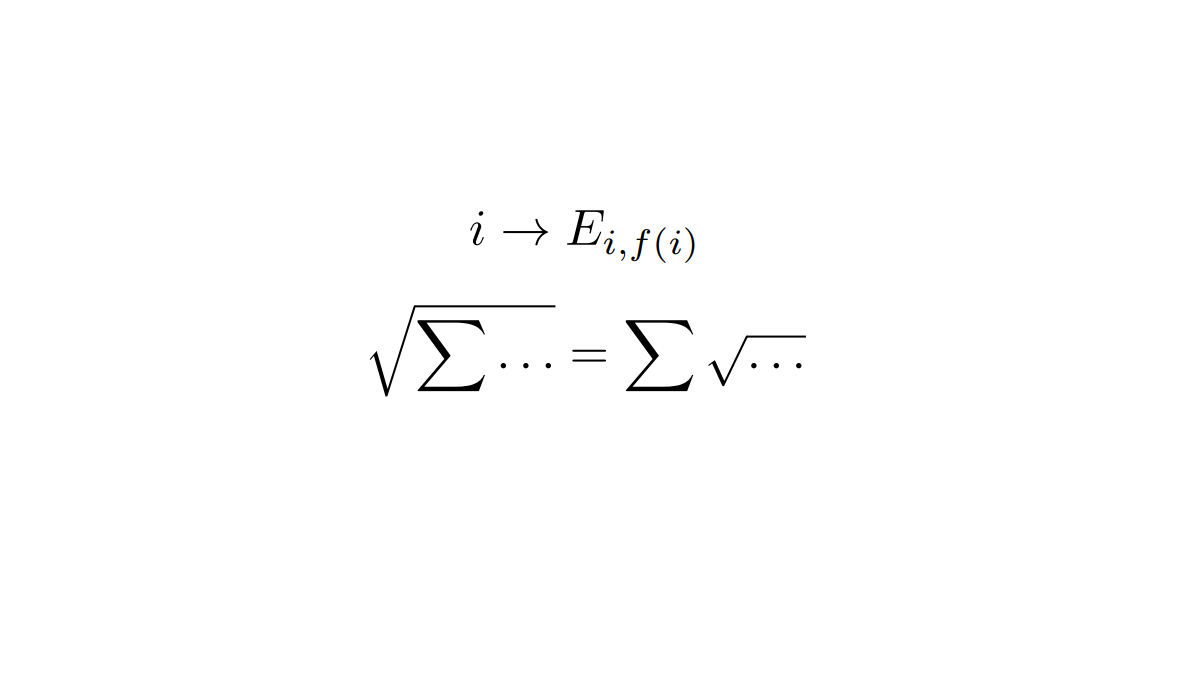VERBAL CALCULATION (VC) IN EVIDENCE-BASED DSS AND NLP

S.B. Pshenichnikov
The article outlines a new mathematical apparatus for verbal calculations in NLP (natural language processing). Words are embedded not in a real vector space, but in an algebra of extremely sparse matrix units. Calculations become evidence-based and transparent. The example shows forks in calculations that go unnoticed when using traditional approaches, and the result may be unexpected.
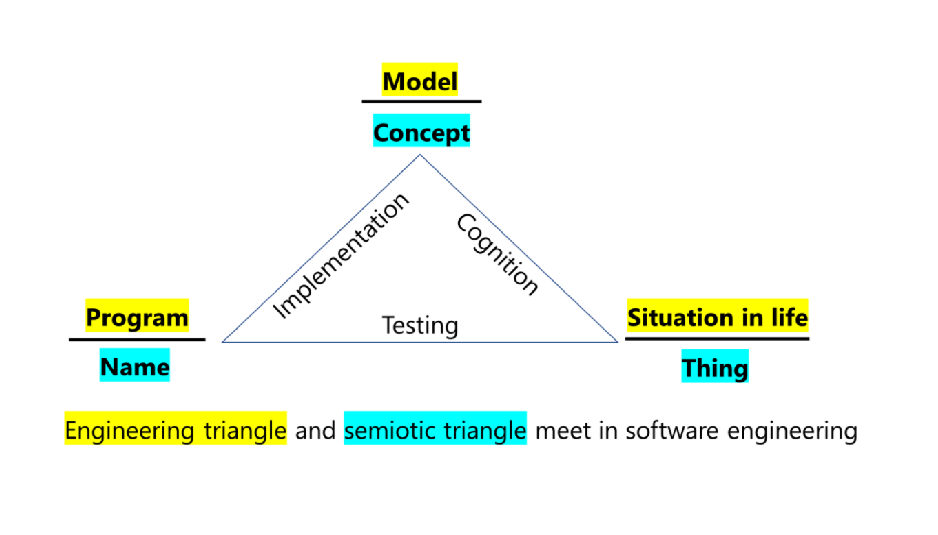
The use of IT in Natural Language Processing (NLP) requires standardization of texts, for example, tokenization or lemmatization.
After this, you can try to use mathematics, since it is the highest form of standardization and turns the objects under study into ideal ones, for example, data tables into matrices of elements. Only in the language of matrices can one search for general patterns in data (numbers and texts).
If text is turned into numbers, then in NLP these are first natural numbers for numbering words, which are then embedded into real vectors is irreversible ed in a real vector space.
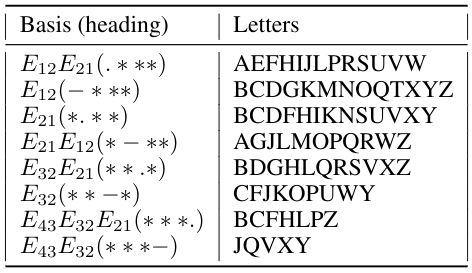
Perhaps we should not rush to do this but come up with a new type of numbers that is more suitable for NLP than numbers for studying physical phenomena. These are matrix hyperbinary numbers. Hyperbinary numbers are one of the types of hypercomplex numbers.
Hyperbinary numbers have their own arithmetic, and if you get used to it, it will seem more familiar and simpler than Pythagorean arithmetic.
In Decision Support Systems (DSS), the texts are value judgments and a numbered verbal rating scale. Next (as in NLP), the numbers are turned into vectors of real numbers and used as sets of weighted arithmetic average coefficients.