Upsetting Opinions about Static Analyzers


General-purpose programming language. It has imperative, object-oriented and generic programming features, while also providing facilities for low-level memory manipulation




There is a story about an experience of using Actor Model in one interesting project of developing an automatic control system for a theatre. Below I'll tell my impressions, no more than that.
According to the description,
Tree-sitter is a parser generator tool and an incremental parsing library. It can build a concrete syntax tree for a source file and efficiently update the syntax tree as the source file is edited.
But how does Tree-sitter handle languages that require a preprocessing stage?
Practically all programming languages are built either on the principle of similarity (to make like this one, only with its own blackjack) or to realize some new concept (modularity, purity of functional calculations, etc.). Or both at the same time.
But in any case, the creator of a new programming language doesn't take his ideas randomly out of thin air. They are still based on his previous experience, obsession with the new concept and other initial settings and constraints.
Is there a minimal set of lexemes, operators, or syntactic constructs that can be used to construct an arbitrary grammar for a modern general-purpose programming language?

Network programming in C++ can be challenging. But even a greater challenge is to find educational content that will arm you with the knowledge on how to apply your networking skills in real applications.
In this article you can learn the basics of socket communication and many ways how you can design your internal messaging protocols.

Asynchronous programming is commonly employed for efficient implementation of network interactions in C++. The essence of this approach lies in the fact that the results of socket read/write functions are not immediately available but become accessible after some time. This approach allows for loading the processor with useful work during the wait for data. Various implementations of this approach exist, such as callbacks, actors, future/promise, coroutines. In C++, these implementations are available as libraries from third-party developers or can be implemented independently.
Coroutines are the most challenging to implement as they require writing platform-dependent code. However, the recent version of the C++ 20 language standard introduces support for coroutines at the compiler and standard library levels. Coroutines are functions that can suspend their execution, preserving their state, and later return to that state to resume the function's work. The compiler automatically creates a checkpoint with the coroutine's state.
For a comprehensive understanding of C++ 20 coroutines, refer to this article. Below, we examine a code example using coroutines and describe important points applied during implementation.

Hash, salt, SHA-1, SHA-2, std::hash.. To a non-programming person that may come up as some kind of a recipe that just does not seem to add up. In a sense, this is indeed supposed to be a gibberish to any third party and a strong, helpful mechanism for us, programmers.
At the start of writing this article, I had one clear idea to get across the table: to finally unveil this mystery of hashing in C++ for beginners. I, a beginner myself, also wanted to solidify my knowledge in this area; so let’s get started.

The point of this article is to explore Lambda functions, their dirrerences from regular functions and how they are implemented, based on C++, Python and Java programming languages.
Throughout this article I will be using godbolt.org to compile code and see machine code or byte code.

Operating systems are a kind of software where code quality is critical. This time the PVS-Studio analyzer checked MuditaOS. So let's take a look at what the static analyzer found in this open-source OS.
We dust off the irregular series of articles about the Chromium project check. Let's look at the code quality in the latest Chromium release and check the new features of the PVS-Studio analyzer.

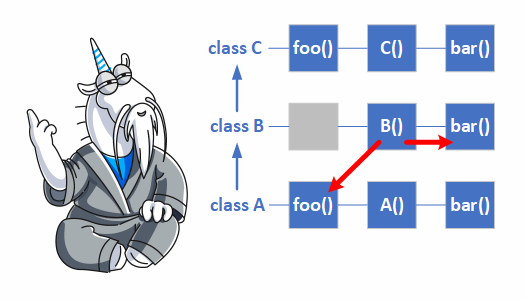
In different programming languages, the behavior of virtual functions differs when it comes to constructors and destructors. Incorrect use of virtual functions is a classic mistake. Developers often use virtual functions incorrectly. In this article, we discuss this classic mistake.
In May 2021, CppCast recorded a podcast called ABI stability (CppCast #300). In this podcast, Marshall Clow and the hosts discussed rather old news — Visual Studio compilers support the AddressSantitzer tool. We have already integrated ASan into our testing system a long time ago. Now we want to tell you about a couple of interesting errors it found.

On August 25th, 2021, the Linux kernel celebrated its 30th anniversary. Since then, it's changed a lot. We changed too. Nowadays, the Linux kernel is a huge project used by millions. We checked the kernel 5 years ago. So, we can't miss this event and want to look at the code of this epic project again.

Stack
Stack is a linear data structure. In stack, data access is limited. It follows the rule of insertion and deletion of data. Stack is a collection of only similar data types. Elements in the stack are arranged sequentially. It follows the LIFO principle which is the last-in and first-out rule.
Example
To understand this concept, let us take an example of arranging coins. If we start placing coins one after the other in such a way that the first coin will be placed first at the bottom and the next coin will come on above the first coin and so on. Now if we want to remove coins, then the topmost coin which is the third coin will be removed first. So in this way, the last coin will be removed first according to the LIFO principle.