Android Robotics up to 2019: The real story; in 5 parts; part 2
How to crack a self-service terminal and why 80% of them are under threat
I always loved playing with things and testing them under all sorts of wacky conditions as a kid and even considered getting a job as a tester, but I never did. Nevertheless, I still like taking things made by someone else and poking them for vulnerabilities.
I remember, when first self-service payment terminals started popping around town, I saw one of them put up a browser window while updating, and the game was on — I broke it almost immediately. There’s been a lot of discussion about it since then and developers have started to pay a lot more attention towards security in these machines.
Recently, fast-food joints have started installing these terminals. Obviously, it’s quite convenient: just tap a couple of virtual buttons, place an order, pay with a bank card and wait for your number to show on the screen.
Also, nearly every big mall has these interactive boards with floor plans and information on various sales and discounts.
How secure are they?
The hard-to-catch bug in LittleBigPlanet

Author of the original post in Russian: HotWaterMusic
The history of the world's gamedev knows quite a few curious bugs that had to be tackled by developers. In fact, judging from the story that Media Molecule's CTO Alex Evans shared on his Twitter page this past weekend, many legends are still waiting to be heard. Evans is famous for his part in a demoscene performance of late 1990s and his work on the LittleBigPlanet game series and on Rag Doll Kung Fu.
The case I am referring to in this article took place ten years ago, in 2008. While working on the first part of LittleBigPlanet — an original puzzle platform video game that was to be released exclusively for PlayStation 3 — the company's developers came across a really hard-to-catch bug.
Normally, for a game to get the green light to be released for consoles, it needs to pass a certification process, i.e. meet a set of requirements predefined by the platform owner. The certification may also include more specific requirements, such as the game running smoothly without crashing for 24 hours.
The development of LittleBigPlanet was at its last stage, with just two weeks to final deployment and distribution. Suddenly a tester from the company's QA in Japan reported that the game was consistently crashing when left overnight. Now the release was evidently out of question unless the bug was fixed.
Robotic Floor Washer

When we think about robots, the first thing that comes to mind are robotic vacuum cleaners. The reason is simple: they are the most "solid" demonstration of success of "consumer" robotics. So making one sounds like a good idea... at first.
But isn't it a bit counter productive - to build something that popular, something we can buy in a store at a commodity (small) price? Should we build something similar, but NOT a vacuum cleaner? Something like... a floor washer, perhaps? Yes, a robotic floor washer.
In this tutorial I am going to build a fully working prototype of a robotic floor washer. By "fully working" I mean that it is going to wash floor, instead of moving dirt around like most robotic "moppers" do. While by "prototype" I mean it is going to be the first step towards production-ready unit, but not a production-ready unit yet. Let me explain.
First of all, it is not going to be THAT solid. You can grab a robotic vacuum cleaner that you got from the store by any part, including wheels and bumper and lift it. It will not fall apart. Ours probably will. The reason is, to make a device "mechanically solid" is a separate task, and if we focus on it, then "robotic" tasks will become more difficult to achieve. So we are going to do what engineers usually do: first they build C3PO without the outside body, wires everywhere and so on. And only then they put a gold-covered outfit on it.
How Much Does It Cost To Create IoT Solution?
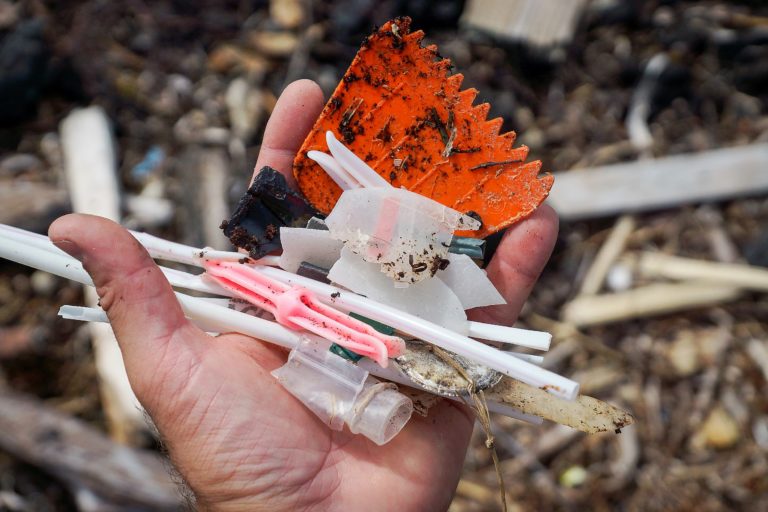
Artificial intelligence takes on ocean trash: Cleaning up the world’s beaches with the help of data
Inspiration sometimes arrives in strange ways. Here is the story of how a dirty disposable diaper led to the development of an artificial intelligence (AI) solution to help rid the world’s coasts of massive amounts of waste and garbage.

Indibiome is the new black
Indibiome is discussed in my previous paper in Russian (link). Shortly indibiome is indigenous microbiome, like indigenous people, term is used below in the meaning «inherent to the media, localised and optimised for sustainable existence»).
Microbes have always been there, however technologies allowing efficient microbes manipulation and accumulated genetic and experimental data on variety of microbial communities has been on the rise only last decade. Below is my concept of interdisciplinary «indibiome bureau» and you are most welcome to give feedback.

Thoughts On Elixir: Pros And Cons Of The Most Popular Tool For High-Load Dev
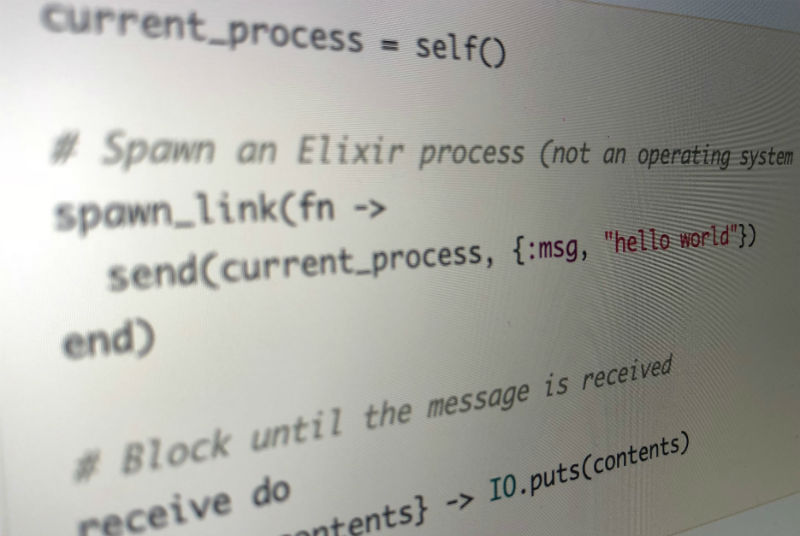
Why is Elixir/Phoenix achieving such a high rate of adoption in the software development industry? What are the best use cases of this language? Are there any drawbacks when using it? We talked to Sergiy Kukunin, a full-stack developer at Spotlight and an Elixir expert, to find answers to these and other questions.
Flightradar24 — how does it work? Part 2, ADS-B protocol

In the first part the basic ideas of operation were described. Now let's go further and figure out, what data is exactly transmitting and receiving between the aircraft and a ground station. We'll also decode this data using Python.
Videogame monsters: how to sow fear
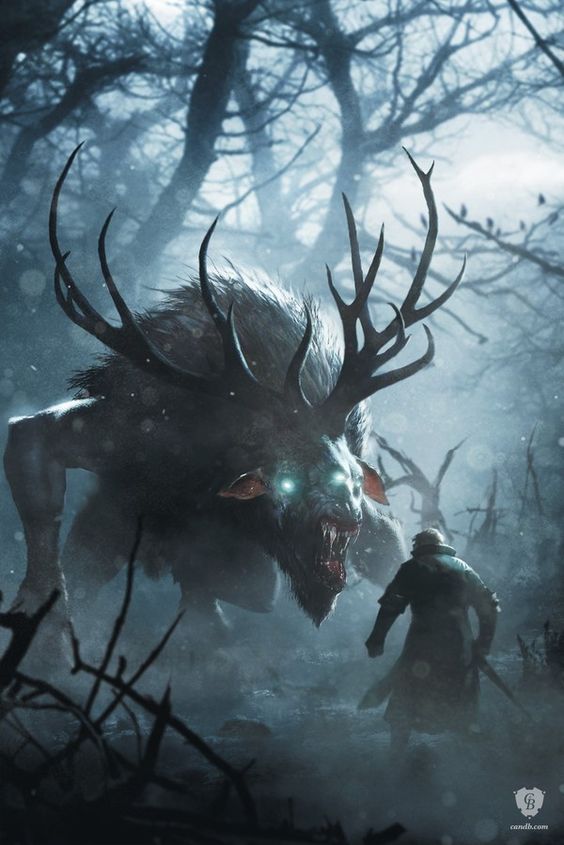

In video games, enemies are one of the key figures, without which a game might lose its meaning, and when it’s not only enemies, but terrifying monsters, they often create the chilling atmosphere intended by the developers. It’s impossible to imagine Silent Hill without the Pyramid Head, or Outlast without Chris Walker, and so on, you get the idea. Monsters are a cumulative image of a video game enemy, and it’s not necessarily an ugly demon or a giant spider: even an angry neighbor, like in Hello Neighbor, is a monster despite his human appearance.
This is where the reader probably asks:
what’s the point of this article?
List of Software Used for Embroidery Digitizing
Because of these benefits, there is a range of software options for you to choose from. This gives you a lot of choices to consider when picking what you want to use. But it can make finding the right one more challenging. Let’s look at some of the best software options to consider.
Hatch
If you’re looking for a leading type of software, you can try Hatch. This is based on three decades of experience. It also has a lot of innovative features that make it easy to use. First, it automatically assigns things like stitch length and placement, to suit the design you create. It also has an automatic branching function, so you’ll be able to sew continuously, rather than in stops and starts.
This software also comes with a lot of tools that are designed to make it easy for you to transform the design onto the computer. For example, you’ll be able to put a hand-drawn sketch into the software. You can also download one of the many existing designs. By doing this, it will be easy for you to create innovative embroidery designs. There are multiple levels, so you’ll only need to pay for the features that you find the most useful.
Energomera CE6806P: Bridging Analog and Digital in Energy Metering

How did engineers in the past manage to measure electrical power without modern microchips and DSPs? This article explores the Energomera CE6806P, a device created in 2006 for verifying electricity meters, yet built using 1980s-era technology.
We’ll take a closer look at its design, principles of operation, and how discrete-analog solutions were used to achieve high accuracy. The Energomera is a fascinating example of engineering and ingenuity, giving us a unique perspective on the evolution of electrical measurement devices.
Hypercube. How we gave developers test devices without losing any
I’m Alexey Lavrenuke. Over the years, I’ve worn many hats: one of the authors behind Yandex.Tank, a speaker on load testing, and the guy who calculated energy consumption by mobile phones. Now I’m a Yandex.Rover developer on the self-driving car team.
After the phones and before Yandex.Rover, there was Hypercube.
A few years ago, the head of mobile development popped in to the load testing department and mentioned a problem they were having with test devices: phones had a tendency to inexplicably migrate from one desk to another. Picking the right device and then finding it had become a challenge. We already experienced working with mobile devices from building a digital ammeter to calculate energy consumption, so we decided to help our coworkers out and quickly rig up a handy contraption. We figured the whole thing wouldn’t take more than three months. Oh how wrong we were. Let me tell you what we were really in for.

''Dallas cube''
Making a demo for NES — HEOHdemo
More than a game: Mastering Mahjong with AI and machine learning
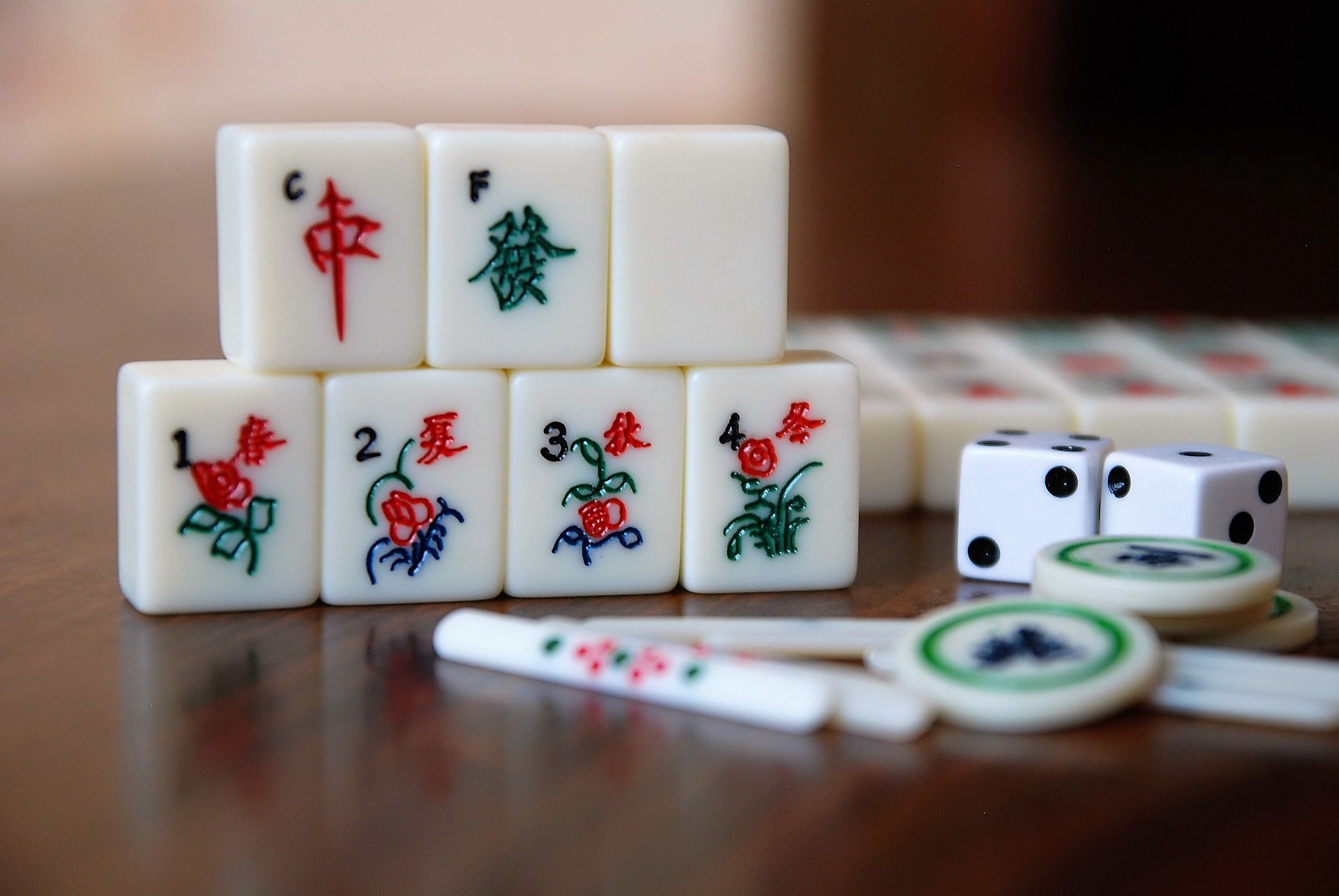

Microsoft researchers have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) system that has taught itself the intricacies of Mahjong and can now match the skills of some of the world’s top players.
The complex board game of chance, bluff, and strategy was invented in China thousands of years ago and remains a passionate pastime for millions of Asians today, with many dedicated competitors playing online.
Computers have learned to play Chess and another ancient Chinese game, Go, amid much fanfare in the past. But scientists at Microsoft Research (MSR) Asia see their achievement as far more than just a case of technology mastering yet another game.
The researchers – who named their system Super Phoenix, or Suphx for short – developed a series of AI algorithmic breakthroughs to navigate the uncertain nature of Mahjong. With more work, these could potentially be applied in real situations to solve problems thrown up by unknown factors and random events.
Python Vs R — Data Science
While a great deal of data researchers will discuss the customary shortcomings like data wrangling in R or data representation in Python, ongoing improvements like Altair for Python or R have adequately reacted to these shortcomings.
So which one would it be a good idea for you to decide for your next data investigation venture?
R has been ruling this space for a long time now. This bodes well as this programming language was explicitly intended for analysts.
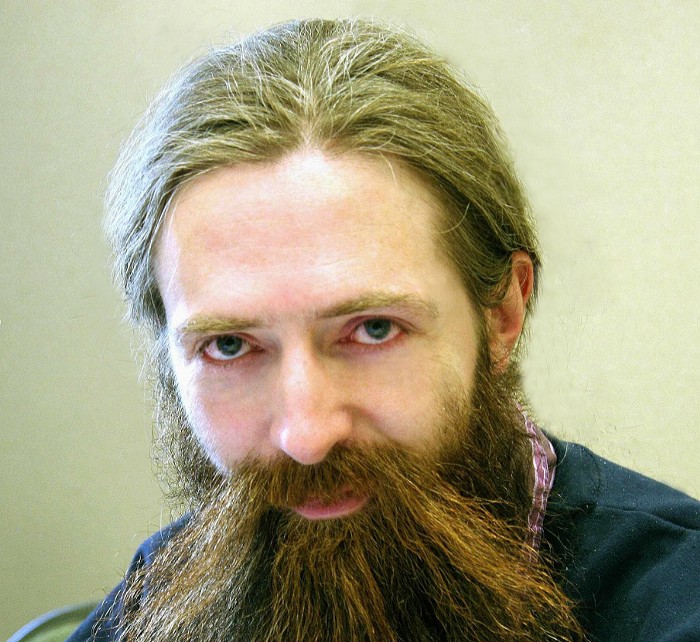
Finally, rejuvenation is a thing

Preface
What is ageing? We can define ageing as a process of accumulation of the damage which is just a side-effect of normal metabolism. While researchers still poorly understand how metabolic processes cause damage accumulation, and how accumulated damage causes pathology, the damage itself – the structural difference between old tissue and young tissue – is categorized and understood pretty well. By repairing damage and restoring the previous undamaged – young – state of an organism, we can really rejuvenate it! It sounds very promising, and so it is. And for some types of damage (for example, for senescent cells) it is already proved to work!
Today in our virtual studio, somewhere between cold, rainy Saint-Petersburg and warm, sunny Mountain View, we meet Aubrey de Grey, again! For those of you who are not familiar with him, here is a brief introduction.
The big interview with Martin Kleppmann: “Figuring out the future of distributed data systems”

Dr. Martin Kleppmann is a researcher in distributed systems at the University of Cambridge, and the author of the highly acclaimed «Designing Data-Intensive Applications» (O'Reilly Media, 2017).
Kevin Scott, CTO at Microsoft once said: «This book should be required reading for software engineers. Designing Data-Intensive Applications is a rare resource that connects theory and practice to help developers make smart decisions as they design and implement data infrastructure and systems.»
Martin’s main research interests include collaboration software, CRDTs, and formal verification of distributed algorithms. Previously he was a software engineer and an entrepreneur at several Internet companies including LinkedIn and Rapportive, where he worked on large-scale data infrastructure.
Vadim Tsesko (@incubos) is a lead software engineer at Odnoklassniki who works in Core Platform team. Vadim’s scientific and engineering interests include distributed systems, data warehouses and verification of software systems.
Contents:
- Moving from business to academic research;
- Discussion of «Designing Data-Intensive Applications»;
- Common sense against artificial hype and aggressive marketing;
- Pitfalls of CAP theorem and other industry mistakes;
- Benefits of decentralization;
- Blockchains, Dat, IPFS, Filecoin, WebRTC;
- New CRDTs. Formal verification with Isabelle;
- Event sourcing. Low level approach. XA transactions;
- Apache Kafka, PostgreSQL, Memcached, Redis, Elasticsearch;
- How to apply all that tools to real life;
- Expected target audience of Martin’s talks and the Hydra conference.
The Role Of Augmented Reality And Virtual Reality In The NBA
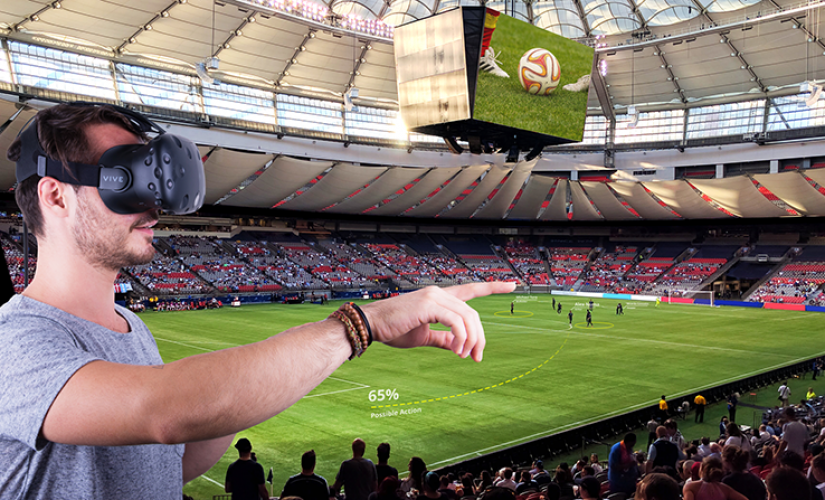

App builders that are looking to achieve a greater level of success will often look to areas that have yet to be explored. Augmented reality and virtual reality are opening up whole new worlds to app builders. For example, there are a number of app builders who are already looking to the NBA in this regard.
The NBA has established a reputation for themselves as a progressive league from a technological standpoint. Teams are already participating in competitive gaming, as numerous franchises have created their own e-sports teams. Now, the league is partnering with app builders to find out more about how they can leverage augmented reality and virtual reality to their benefit.
Hubs
Authors' contribution
alizar 121057.6marks 91318.1lozga 26676.6Zelenyikot 25529.0ivansychev 17563.2AlexeyNadezhin 17349.2Seleditor 14024.1Dmytro_Kikot 13177.0Erwinmal 12741.0Tylerskald 12117.0