Armenia is a lucky country. Back in the 1990s somebody lobbied Synopsys, the #1 leader in the Electronic Design Automation market, to create a division there. It was joined by Mentor Graphics / Siemens EDA, another EDA leader, then NVidia. Synopsys Armenia became the largest Synopsys division outside the US Silicon Valley and Boston, although the Taiwanese may tell you otherwise. Since Synopsys and Mentor make software used by chip designers in Apple, Samsung, AMD and all other electronic companies, Armenia has an unfair advantage over all their neighbors in Caucasus and Central Asia.
In addition, Armenia has friendly relations with Russia, and most Armenians speak Russian as well. This has facilitated the move of many Russian companies to Armenia, for example, a RISC-V semiconductor IP provider Syntacore. Finally, as we can see from the recent conference EDA Connect, Armenia is attracting the attention of electronic and EDA companies from China.
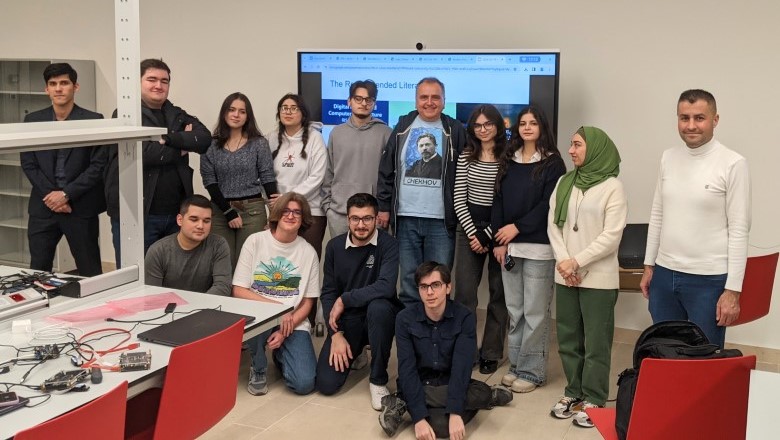
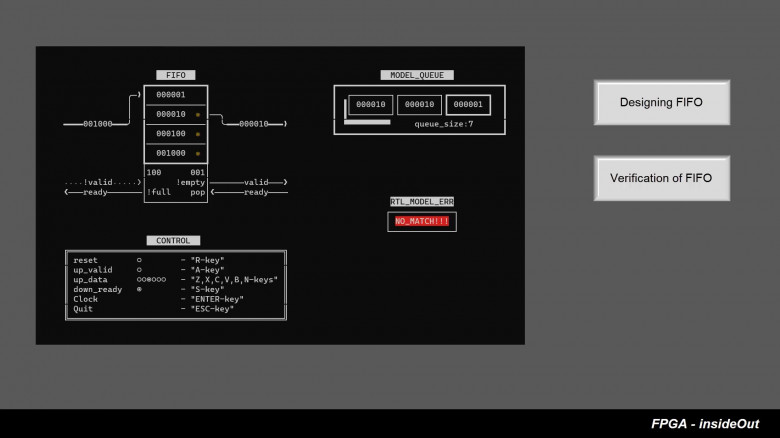
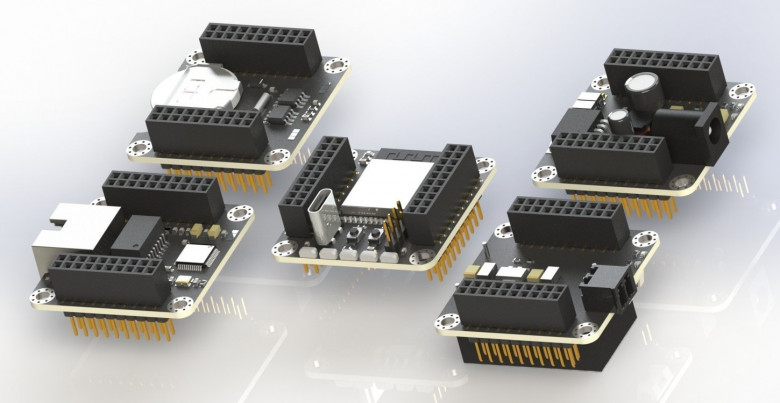
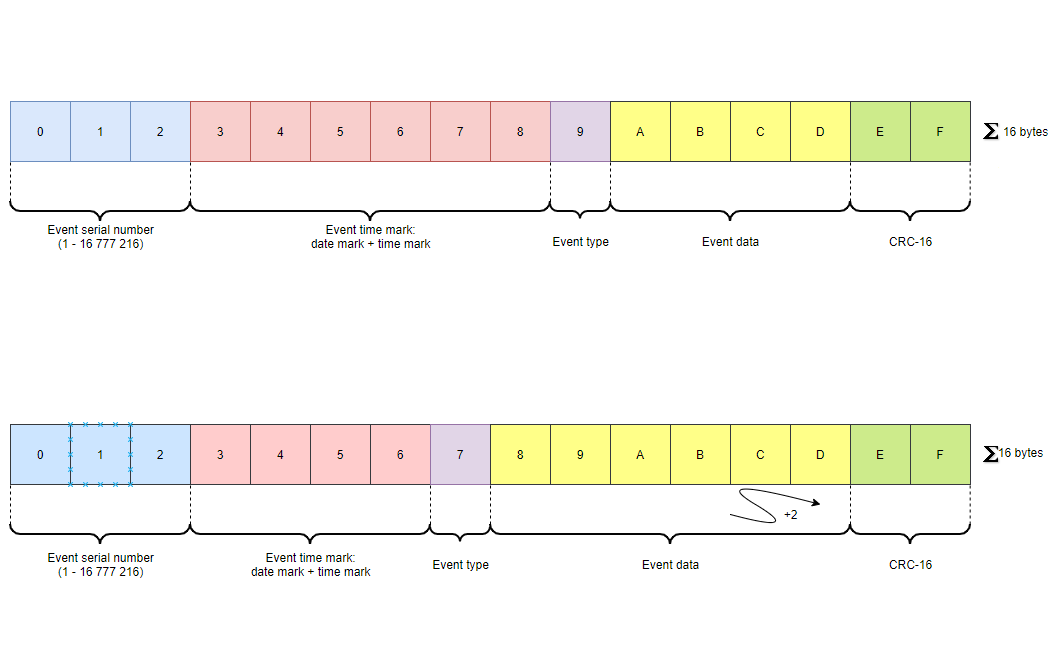
EDA Connect featured not only academic and industrial papers but also a hackathon on FPGA design, attended by local students from Yerevan State University, the American University of Armenia, the Russian-Armenian University, the French University in Armenia and others.