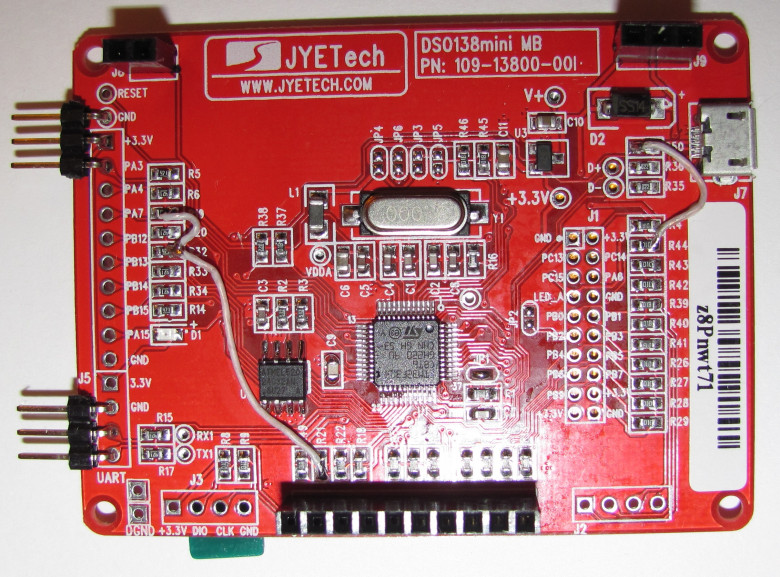
On Ali, an interesting toy – an oscilloscope called DSO138 is sold for a very inexpensive price. It has already gained quite a lot of popularity among electronics lovers, but the parameters of this device, alas, allow it to be more or less fully used only for debugging very low-frequency circuits. Actually, it is not positioned as a tool, but rather as a DIY-kit for novice electronics engineers.
This "toy" oscilloscope is assembled on the STM32F103 microcontroller, and with a fairly competent circuit design of the digital part, the presence of a fairly decent 320X240-dot color display, and not the most rotten analog path, everything, alas, is ruined by very weak ADCs on board the 32F103. The claimed band of 200 kHz can be recognized as such only with a very large stretch. Yes, it will show the presence or absence of a signal with such a frequency, but it will not be possible to really look at something beyond this.
At the same time, the 103-series has a slightly more powerful brother - the STM32F303, it is almost completely compatible with the legs, but it is significantly better in terms of the parameters we are interested in, there are 4 ADCs on board with a conversion frequency of 5 MHz (6 MHz with a 10-bit resolution). In this scenario, if you use all 4 ADCs in parallel with a 10-bit resolution, you can get a effective resolution of up to an honest 24 MSPS (millions of samples per second). The microcontroller is also inexpensive; you can easily find it on the same Ali for very reasonable money again. It is clear that the idea to change the microcontroller arose almost immediately after I tried this DSO138.
At the same time, if upgraded the toy can turn out to be a completely full-fledged tool that even professionals, not just novice amateurs, could already use. With these thoughts in mind, I decided to try to do something with a Chinese toy in my free time.